The study of volume density of tracheal ganglions in vitro in new born babies with respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 20002001
- PMCID: PMC5603691
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2009.2790
The study of volume density of tracheal ganglions in vitro in new born babies with respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
Volume density of respiratory organs was studied in vitro in newborn babies at different age of gestation (abort, immature, premature and mature) using stereometric method. The total of 23 cases was subject to this study. The respiratory organs (trachea, lungs) were taken from autopsies of newborn babies exited from different causes. For this purpose the tissues were fixed in formalin (10%) solution, cut serially in 7micro and 10micro slabs. Volume density of the respiratory system was assessed stereometricaly using Universal testing system Weibel M 42. We observed that volume density of epithelia, musculature and glands were proportionally present in the tracheal tissue. Cellular interstitial tissue is consistently increasing and corresponds to the developmental stages of the newborn babies. The density of tracheal ganglions is greater in premature ages of immature and premature newborns (p<0,05). Decreased number of ganglion cells is observed in mature ages (p<0,05). This is caused by intensive ramification of ganglions from serosa to deeper layers of trachea right to epithelium. Medium diameter of tracheal ganglions is greater in mature newborn babies and corresponds to developmental ages of babies.
Figures



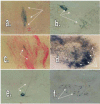
Cholinereactivity well expressed in perichondrial mature ganglion containing 21 ganglion cells in mature babies (Indoxyl method for esterase; 650x).
Ganglion cells in lamina propria of tracheal tissue with expressed choline reactivity, with dendritic and axonal extensions around tracheal glands in prematurely born babies (Indoxyl method for esterase; 400 x).
Choline reactivity in smooth musculature tracheal ganglion in prematurely born babies, which contains 4 cells with oval appearance (Indoxyl method for esterase; 400 x).
Tracheal ganglion cells arranged in the crown form with expressed choline reactivity in mature born babies (Indoxyl method for esterase; 1600 x).
Ganglion cells in lamina propria of tracheal tissue with axonal extension (Indoxyl method for esterase; 400 x).
Group of ganglion cells with perivascular arrangement in tracheal tissue in prematurely born babies (Indoxyl method for esterase; 650x).
Similar articles
-
Examination of ontogenetic-morphologic growth of adrenergic receptor system in the isolated preparation of trachea in vitro.Med Arh. 2008;62(4):200-4. Med Arh. 2008. PMID: 19145801
-
In vitro examination of degenerative evolution of adrenergic nerve endings in pulmonary inflammatory [corrected] processes in newborns.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2008 Aug;8(3):220-5. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2008.2921. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 18816252 Free PMC article.
-
[Examination of ontogenetic-morphologic growth of cholinergic receptor system in isolated preparation of human trachea in vitro].Med Arh. 2006;60(1):13-7. Med Arh. 2006. PMID: 16425526 Bosnian.
-
Lethal severe congenital tracheal stenosis with tracheal ring complicating respiratory distress syndrome in an extremely premature infant: first reported case in Qatar with a literature review.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Dec 12;13(12):e236107. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236107. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33310828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in pathologic aspects of neonatal respiratory distress.Pathol Annu. 1973;8:407-52. Pathol Annu. 1973. PMID: 4598175 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baluk P, Fujiwara T, Matsuda S. The fine structure of the ganglia of the guinea-pig trachea. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239:51–60. - PubMed
-
- John W.M. Neurogenesis of patterns for neurogenesis of gasping:noeud vital or noeuds vitals. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996;81:1865–1877. - PubMed
-
- Shabani R, Hundozi Z, Islami H. Evoluimi i dendësisë numerike neuronale në bëthamat dorsale motorike dhe solitare të nervit vagus në palcën e zgjatur te të porsalindurit. Praxix medica. 2002;44:10–17.
-
- Shibata K, Taketani K. Excitatory effect of noradrenaline on rat airway parasympathetic ganglion neurons. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi, 2001;92:377–383. - PubMed

