Differential actions of urocortins on neurons of the myenteric division of the enteric nervous system in guinea pig distal colon
- PMID: 20002096
- PMCID: PMC2823367
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00516.x
Differential actions of urocortins on neurons of the myenteric division of the enteric nervous system in guinea pig distal colon
Abstract
Background and purpose: Urocortins (Ucns) 1, 2 and 3 are corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-related neuropeptides and may be involved in neural regulation of colonic motor functions. Nevertheless, details of the neural mechanism of action for Ucns have been unclear. We have, here, tested the hypothesis that Ucns act in the enteric nervous system (ENS) to influence colonic motor behaviour.
Experimental approach: We used intracellular recording with 'sharp' microelectrodes, followed by intraneuronal injection of biocytin, and immunohistochemical localization of CRF(1) and CRF(2) receptors in guinea pig colonic tissue.
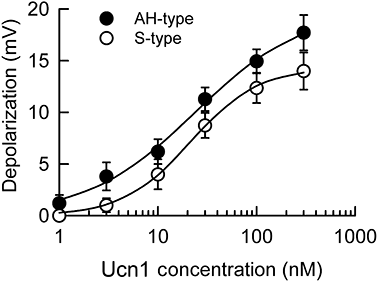
Key results: Application of Ucn1 depolarized membrane potentials and elevated excitability in 58% of AH-type and 60% of S-type colonic myenteric neurons. In most of the neurons tested, depolarizing responses evoked by Ucn-1 were suppressed by the CRF(1) receptor antagonist NBI 27914, but were unaffected by the CRF(2) receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30. The selective CRF(2) receptor agonists, Ucn2 and Ucn3, evoked depolarizing responses in 12 and 8% of the AH-type myenteric neurons, respectively, and had no effect on S-type neurons. Antisauvagine-30, but not NBI 27914, suppressed these Ucn2- and Ucn3-evoked responses. Immunohistochemical staining identified CRF(1) as the predominant CRF receptor subtype expressed by ganglion cell somas, while CRF(2)-immunoreactive neuronal somas were sparse. Ucns did not affect excitatory synaptic transmission in the ENS.
Conclusions and implications: The results suggest that Ucns act as neuromodulators to influence myenteric neuronal excitability. The excitatory action of Ucn1 in myenteric neurons was primarily at CRF(1) receptors, and the excitatory action of Ucn2 and Ucn3 was at CRF(2) receptors.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Expression of type 1 corticotropin-releasing factor receptor in the guinea pig enteric nervous system.J Comp Neurol. 2005 Jan 17;481(3):284-98. doi: 10.1002/cne.20370. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15593376
-
Distribution and chemical coding of corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive neurons in the guinea pig enteric nervous system.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Jan 1;494(1):63-74. doi: 10.1002/cne.20781. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16304680 Free PMC article.
-
Urocortin I is present in the enteric nervous system and exerts an excitatory effect via cholinergic and serotonergic pathways in the rat colon.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):G903-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00066.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17717045
-
Urocortins: CRF's siblings and their potential role in anxiety, depression and alcohol drinking behavior.Alcohol. 2012 Jun;46(4):349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2011.10.007. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 22444954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urocortins: Actions in health and heart failure.Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Nov;474:76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Clin Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 28887029 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain and Gut CRF Signaling: Biological Actions and Role in the Gastrointestinal Tract.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018;11(1):51-71. doi: 10.2174/1874467210666170224095741. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28240194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urocortin 1 modulates immunosignaling in a rat model of colitis via corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 2.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):G884-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00319.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21330446 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin releasing factor signaling in colon and ileum: regulation by stress and pathophysiological implications.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;60 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):33-46. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20388944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Otilonium Bromide Prevents Cholinergic Changes in the Distal Colon Induced by Chronic Water Avoidance Stress, a Rat Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 18;24(8):7440. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087440. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108603 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Stress, Inflammation, and Colon Cancer: A CRH System-Driven Molecular Crosstalk.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 12;8(10):1669. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101669. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31614860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:525–357. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Kunze WA, Bornstein JC, Furness JB, Smith ML. Analysis of the responses of myenteric neurons in the small intestine to chemical stimulation of the mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:G422–G435. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Kunze WA, Bornstein JC, Furness JB. Electrical mapping of the projections of intrinsic primary afferent neurones to the mucosa of the guinea-pig small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1998;10:533–541. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Kunze WA, Furness JB, Bornstein JC. The terminals of myenteric intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the guinea-pig ileum are excited by 5-hydroxytryptamine acting at 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 receptors. Neuroscience. 2000;101:459–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

