Arachidonic acid release mediated by OX1 orexin receptors
- PMID: 20002100
- PMCID: PMC2823366
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00535.x
Arachidonic acid release mediated by OX1 orexin receptors
Abstract
Background and purpose: We have previously shown that lipid mediators, produced by phospholipase D and C, are generated in OX(1) orexin receptor signalling with high potency, and presumably mediate some of the physiological responses to orexin. In this study, we investigated whether the ubiquitous phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) signalling system is also involved in orexin receptor signalling.
Experimental approach: Recombinant Chinese hamster ovary-K1 cells, expressing human OX(1) receptors, were used as a model system. Arachidonic acid (AA) release was measured from (3)H-AA-labelled cells. Ca(2+) signalling was assessed using single-cell imaging.
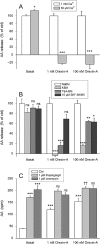
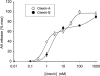
Key results: Orexins strongly stimulated [(3)H]-AA release (maximally 4.4-fold). Orexin-A was somewhat more potent than orexin-B (pEC(50) = 8.90 and 8.38 respectively). The concentration-response curves appeared biphasic. The release was fully inhibited by the potent cPLA(2) and iPLA(2) inhibitor, methyl arachidonyl fluorophosphonate, whereas the iPLA(2) inhibitors, R- and S-bromoenol lactone, caused only a partial inhibition. The response was also fully dependent on Ca(2+) influx, and the inhibitor studies suggested involvement of the receptor-operated influx pathway. The receptor-operated pathway, on the other hand, was partially dependent on PLA(2) activity. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase, but not protein kinase C, were involved in the PLA(2) activation at low orexin concentrations.
Conclusions and implications: Activation of OX(1) orexin receptors induced a strong, high-potency AA release, possibly via multiple PLA(2) species, and this response may be important for the receptor-operated Ca(2+) influx. The response coincided with other high-potency lipid messenger responses, and may interact with these signals.
Figures


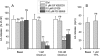

Similar articles
-
OX1 orexin/hypocretin receptor activation of phospholipase D.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4b):1109-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01565.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21718304 Free PMC article.
-
OX1 orexin/hypocretin receptor signaling through arachidonic acid and endocannabinoid release.Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;82(2):156-67. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.078063. Epub 2012 May 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22550093
-
OX1 orexin receptors activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase in Chinese hamster ovary cells via multiple mechanisms: the role of Ca2+ influx in OX1 receptor signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Jan;20(1):80-99. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0389. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16141359
-
Lipid signaling cascades of orexin/hypocretin receptors.Biochimie. 2014 Jan;96:158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 23810911 Review.
-
Orexins/hypocretins: pain regulation and cellular actions.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(28):3089-100. doi: 10.2174/138161210793292483. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20687883 Review.
Cited by
-
Orexin receptors in GtoPdb v.2021.3.IUPHAR BPS Guide Pharm CITE. 2021;2021(3):10.2218/gtopdb/f51/2021.3. doi: 10.2218/gtopdb/f51/2021.3. Epub 2021 Sep 2. IUPHAR BPS Guide Pharm CITE. 2021. PMID: 34927075 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling cascades.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;171(2):314-31. doi: 10.1111/bph.12324. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23902572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OX1 orexin/hypocretin receptor activation of phospholipase D.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4b):1109-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01565.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21718304 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin/hypocretin based pharmacotherapies for the treatment of addiction: DORA or SORA?CNS Drugs. 2014 Aug;28(8):713-30. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0179-x. CNS Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24942635 Review.
-
Orexin A stimulates glucose uptake, lipid accumulation and adiponectin secretion from 3T3-L1 adipocytes and isolated primary rat adipocytes.Diabetologia. 2011 Jul;54(7):1841-52. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2152-2. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21505958
References
-
- Akiba S, Sato T. Cellular function of calcium-independent phospholipase A2. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:1174–1178. - PubMed
-
- Ammoun S, Holmqvist T, Shariatmadari R, Oonk HB, Detheux M, Parmentier M, et al. Distinct recognition of OX1 and OX2 receptors by orexin peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:507–514. - PubMed
-
- Ammoun S, Johansson L, Ekholm ME, Holmqvist T, Danis AS, Korhonen L, et al. OX1 orexin receptors activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in CHO cells via multiple mechanisms: The role of Ca2+ influx in OX1 receptor signaling. Mol Endocrinol. 2006a;20:80–99. - PubMed
-
- Ammoun S, Lindholm D, Wootz H, Åkerman KE, Kukkonen JP. G-protein-coupled OX1 orexin/hcrtr-1 hypocretin receptors induce caspase-dependent and -independent cell death through p38 mitogen-/stress-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2006b;281:834–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

