Chronic cortical and subcortical pathology with associated neurological deficits ensuing experimental herpes encephalitis
- PMID: 20002440
- PMCID: PMC2895975
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00354.x
Chronic cortical and subcortical pathology with associated neurological deficits ensuing experimental herpes encephalitis
Abstract
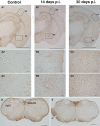
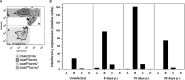
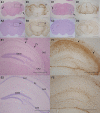
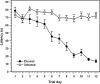
Long-term neurological sequela is common among herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE) survivors. Animal models for HSE are used to investigate mechanisms of acute disease, but little has been done to model chronic manifestations of HSE. The current study presents a detailed, systematic analysis of chronic neuropathology, including characterization of topography and sequential progression of degenerative lesions and inflammation. Subsequent to intranasal HSV-1 infection, inflammatory responses that were temporally and spatially distinct persisted in infected cortical and brain stem regions. Neutrophils were present exclusively within the olfactory bulb and brain stem regions during the acute phase of infection, while the chronic inflammation was marked by plasma cells, lymphocytes and activated microglia. The chronic lymphocytic infiltrate, cytokine production, and activated microglia were associated with the loss of cortical neuropile in the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus. Animals surviving the acute infection showed a spectrum of chronic lesions from decreased brain volume, neuronal loss, activated astrocytes, and glial scar formation to severe atrophy and cavitations of the cortex. These lesions were also associated with severe spatial memory deficits in surviving animals. Taken together, this model can be utilized to further investigate the mechanisms of neurological defects that follow in the wake of HSE.
Figures
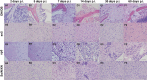
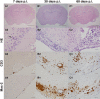
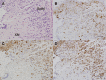
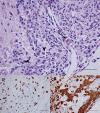
References
-
- Anderson JR, Field HJ (1983) The distribution of herpes simplex type 1 antigen in mouse central nervous system after different routes of inoculation. J Neurol Sci 60:181–195. - PubMed
-
- Aurelius E, Andersson B, Forsgren M, Skoldenberg B, Strannegard O (1994) Cytokines and other markers of intrathecal immune response in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Infect Dis 170:678–681. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee K, Biswas PS, Kim B, Lee S, Rouse BT (2004) CXCR2‐/‐ mice show enhanced susceptibility to herpetic stromal keratitis: a role for IL‐6‐induced neovascularization. J Immunol 172:1237–1245. - PubMed
-
- Baringer JR (2008) Herpes simplex infections of the nervous system. Neurol Clin 26:657–674. - PubMed
-
- Beers DR, Henkel JS, Schaefer DC, Rose JW, Stroop WG (1993) Neuropathology of herpes simplex virus encephalitis in a rat seizure model. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:241–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

