Differential modulation of mu-opioid receptor signaling to adenylyl cyclase by regulators of G protein signaling proteins 4 or 8 and 7 in permeabilised C6 cells is Galpha subtype dependent
- PMID: 20002516
- PMCID: PMC2947325
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06519.x
Differential modulation of mu-opioid receptor signaling to adenylyl cyclase by regulators of G protein signaling proteins 4 or 8 and 7 in permeabilised C6 cells is Galpha subtype dependent
Abstract
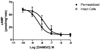
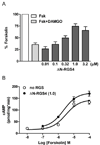
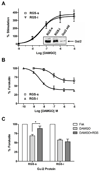
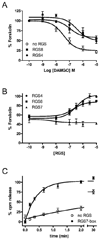
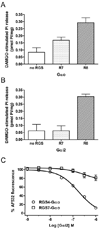
Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins act as GTPase-accelerating protein to negatively modulate G protein signaling and are defined by a conserved RGS domain with considerable amino acid diversity. To determine the effects of specific, purified RGS proteins on mu-opioid signaling, C6 cells stably expressing a mu-opioid receptor were rendered permeable to proteins by treatment with digitonin. Mu-opioid inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylyl cyclase by [D-Ala(2),N-Me-Phe(4),Gly-ol]-enkephalin (DAMGO), a mu-specific opioid peptide, remained fully intact in permeabilized cells. Purified RGS domain of RGS4 added to permeabilized cells resulted in a twofold loss in DAMGO potency but had no effect in cells expressing RGS-insensitive G proteins. The inhibitory effect of DAMGO was reduced to the same extent by purified RGS4 and RGS8. In contrast, the RGS domain of RGS7 had no effect and inhibited the action of RGS8 as a result of weak physical association with Galphai2 and minimal GTPase-accelerating protein activity in C6 cell membranes. These data suggest that differences in conserved RGS domains of specific RGS proteins contribute to differential regulation of opioid signaling to adenylyl cyclase and that a permeabilized cell model is useful for studying the effects of specific RGS proteins on aspects of G protein-coupled receptor signaling.
Figures
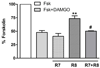
Similar articles
-
μ-Opioid receptors and regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins: from a symposium on new concepts in mu-opioid pharmacology.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Mar 1;121(3):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.10.027. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 22129844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous regulators of G protein signaling differentially modulate full and partial mu-opioid agonists at adenylyl cyclase as predicted by a collision coupling model.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 May;73(5):1538-48. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043547. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18285510
-
Endogenous regulator of g protein signaling proteins reduce {mu}-opioid receptor desensitization and down-regulation and adenylyl cyclase tolerance in C6 cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Feb;312(2):809-15. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.074641. Epub 2004 Sep 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15383633
-
Endogenous RGS protein action modulates mu-opioid signaling through Galphao. Effects on adenylyl cyclase, extracellular signal-regulated kinases, and intracellular calcium pathways.J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 14;278(11):9418-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208885200. Epub 2003 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12524446
-
Assays for G-protein-coupled receptor signaling using RGS-insensitive Galpha subunits.Methods Enzymol. 2004;389:155-69. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)89010-4. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 15313565 Review.
Cited by
-
Mu opioid receptor activation enhances regulator of G protein signaling 4 association with the mu opioid receptor/G protein complex in a GTP-dependent manner.J Neurochem. 2015 Oct;135(1):76-87. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13222. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26119705 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of G-proteins and G-protein Regulating Proteins in Depressive Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 13;9:1289. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01289. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30483131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic mouse models in opioid research: current status and future directions.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024 May;131(5):491-494. doi: 10.1007/s00702-024-02762-6. Epub 2024 Mar 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024. PMID: 38436758 Review.
-
Regulators of G-Protein Signaling (RGS) Proteins Promote Receptor Coupling to G-Protein-Coupled Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (GIRK) Channels.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 10;38(41):8737-8744. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0516-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 27. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30150362 Free PMC article.
-
μ-Opioid receptors and regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins: from a symposium on new concepts in mu-opioid pharmacology.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Mar 1;121(3):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.10.027. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 22129844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alt A, McFadyen IJ, Fan CD, Woods JH, Traynor JR. Stimulation of guanosine-5'-o-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate binding in digitonin-permeabilized C6 rat glioma cells: evidence for an organized association of mu-opioid receptors and G protein. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001;298:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Brooker G, Pedone C. Maintenance of whole cell isoproterenol and forskolin responsiveness in adenylate cyclase of permeabilized cells. J. Cyclic. Nucleotide. Protein Phosphor. Res. 1986;11:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Chao J, Nestler EJ. Molecular neurobiology of drug addiction. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004;55:113–132. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier N, Prezeau L, Carrette J, Bertorelli R, Le CG, Manzoni O, Bockaert J, Homburger V. Transfected Go1 alpha inhibits the calcium dependence of beta-adrenergic stimulated cAMP accumulation in C6 glioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:8980–8989. - PubMed
-
- Clark MJ, Furman CA, Gilson TD, Traynor JR. Comparison of the relative efficacy and potency of mu-opioid agonists to activate Galpha(i/o) proteins containing a pertussis toxin-insensitive mutation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006;317:858–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

