Periadventitial delivery of anti-EGF receptor antibody inhibits neointimal macrophage accumulation after angioplasty in a hypercholesterolaemic rabbit
- PMID: 20002649
- PMCID: PMC2884090
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00700.x
Periadventitial delivery of anti-EGF receptor antibody inhibits neointimal macrophage accumulation after angioplasty in a hypercholesterolaemic rabbit
Abstract
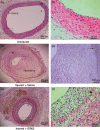
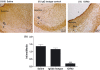
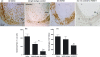
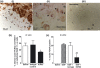
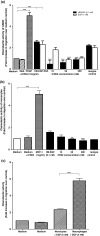
Monocyte recruitment and their differentiation into macrophages are both early events in native and accelerated atherosclerosis that follows angioplasty. We have investigated the putative functional role of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) present on rabbit monocytes/macrophages. The impact of periadventitial delivery of an EGFR-specific, blocking monoclonal antibody (ICR62, which inhibits EGF-binding to its receptor) was investigated in a rabbit model of accelerated atherosclerosis induced by a combination of carotid injury and 4 weeks of a 2% cholesterol-diet. Two weeks after the initiation of the diet, a balloon-catheter angioplasty of the left common carotid artery was performed and a collar placed around the injured carotid artery immediately, for the delivery of ICR62 antibody, isotype-matched antibody or saline control. Monocyte/macrophage accumulation, cell proliferation and neointimal thickening were determined 2 weeks after the delivery of the antibodies. The function of the EGFR on rabbit monocytes was also investigated in vitro, using chemotaxis assays. Treatment with ICR62 was associated with a significant reduction in macrophage accumulation and neointimal thickening and a 76% reduction in neointimal area of the vessel wall compared with controls. In vitro ICR62 inhibited macrophage and smooth muscle cell migration towards EGFR ligands including EGF and HB-EGF. These findings suggest that EGFR ligation may be important in the development of early atherosclerotic lesions following balloon-catheter angioplasty, and periadventitial delivery may provide a feasible approach for administration of the inhibitors of EGFR-binding such as ICR62.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil, not macrophage, infiltration precedes neointimal thickening in balloon-injured arteries.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000 Dec;20(12):2553-8. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.12.2553. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000. PMID: 11116052
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of radiation inhibition of restenosis. Part I: role of the macrophage and platelet-derived growth factor.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998 Mar 1;40(4):929-41. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(97)00937-1. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998. PMID: 9531379
-
Placental growth factor promotes atherosclerotic intimal thickening and macrophage accumulation.Circulation. 2005 May 31;111(21):2828-36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.495887. Epub 2005 May 23. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15911697
-
The role of hyaluronan and its receptors in restenosis after balloon angioplasty: development of a potential therapy.Int J Tissue React. 1995;17(4):141-51. Int J Tissue React. 1995. PMID: 8867644 Review.
-
Intimal hyperplasia in murine models.Curr Drug Targets. 2008 Mar;9(3):251-60. doi: 10.2174/138945008783755601. Curr Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18336244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Its Ligands in Kidney Inflammation and Damage.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 23;2018:8739473. doi: 10.1155/2018/8739473. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30670929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of key regulators and downstream targets of E. coli induced mastitis.J Appl Genet. 2019 Nov;60(3-4):367-373. doi: 10.1007/s13353-019-00499-7. Epub 2019 Jun 11. J Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 31187384
-
Ticagrelor Improves Endothelial Function by Decreasing Circulating Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF).Front Physiol. 2018 Apr 6;9:337. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00337. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29686623 Free PMC article.
-
Mig-6 gene knockout induces neointimal hyperplasia in the vascular smooth muscle cell.Dis Markers. 2014;2014:549054. doi: 10.1155/2014/549054. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Dis Markers. 2014. PMID: 25574067 Free PMC article.
-
Association of ACE gene polymorphisms with in-stent restenosis by stent type (biomime, supraflex, xience).Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Aug;50(8):6445-6455. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08554-7. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37328581
References
-
- Biwa T, Sakai M, Shichiri M, Horiuchi S. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plays an essential role in oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced macrophage proliferation. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2000;7:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Chan AK, Kalmes A, Hawkins S, Daum G, Clowes AW. Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor decreases intimal hyperplasia in balloon-injured rat carotid artery. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003;37:644–649. - PubMed
-
- Charo IF, Taubman MB. Chemokines in the pathogenesis of vascular disease. Circ. Res. 2004;95:858–866. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham MP, Thomas H, Fan Z, Modjtahedi H. Responses of human colorectal tumor cells to treatment with the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody ICR62 used alone and in combination with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2006;66:7708–7715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

