Hospitalization risk following initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 20002778
- PMCID: PMC3077939
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2009.00776.x
Hospitalization risk following initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
Objectives: While highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) decreases long-term morbidity and mortality, its short-term effect on hospitalization rates is unknown. The primary objective of this study was to determine hospitalization rates over time in the year after HAART initiation for virological responders and nonresponders.
Methods: Hospitalizations among 1327 HAART-naïve subjects in an urban HIV clinic in 1997-2007 were examined before and after HAART initiation. Hospitalization rates were stratified by virological responders (> or =1 log(10) decrease in HIV-1 RNA within 6 months after HAART initiation) and nonresponders. Causes were determined through International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision (ICD-9) codes and chart review. Multivariate negative binomial regression was used to assess factors associated with hospitalization.
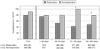
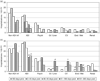
Results: During the first 45 days after HAART initiation, the hospitalization rate of responders was similar to their pre-HAART baseline rate [75.1 vs. 78.8/100 person-years (PY)] and to the hospitalization rate of nonresponders during the first 45 days (79.4/100 PY). The hospitalization rate of responders fell significantly between 45 and 90 days after HAART initiation and reached a plateau at approximately 45/100 PY from 91 to 365 days after HAART initiation. Significant decreases were seen in hospitalizations for opportunistic and nonopportunistic infections.
Conclusions: The first substantial clinical benefit from HAART may be realized by 90 days after HAART initiation; providers should keep close vigilance at least until this time.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: RDM has been a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb and GlaxoSmithKline and has received research funding from Merck, Pfizer, and Gilead. KAG has been a consultant for Tibotec and has also received research funding unrelated to this project from Tibotec. Both other authors: no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Buchacz K, Baker RK, Moorman AC, et al. Rates of hospitalizations and associated diagnoses in a large multisite cohort of HIV patients in the United States, 1994–2005. AIDS. 2008;22:1345–1354. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Baker RK, Moorman AC, et al. Mortality in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era: changing causes of death and disease in the HIV outpatient study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006;43:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Porter K, Babiker A, Bhaskaran K, Darbyshire J, Pezzotti P, Walker AS. Determinants of survival following HIV-1 seroconversion after the introduction of HAART. Lancet. 2003;362:1267–1274. - PubMed
-
- Gebo KA, Fleishman JA, Moore RD. Hospitalizations for metabolic conditions, opportunistic infections, and injection drug use among HIV patients: trends between 1996 and 2000 in 12 states. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;40:609–616. - PubMed
-
- Gebo KA, Diener-West M, Moore RD. Hospitalization rates differ by hepatitis C status in an urban HIV cohort. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;34:165–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

