Identification of small molecule compounds that inhibit the HIF-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 20003191
- PMCID: PMC2797767
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-117
Identification of small molecule compounds that inhibit the HIF-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is the major hypoxia-regulated transcription factor that regulates cellular responses to low oxygen environments. HIF-1 is composed of two subunits: hypoxia-inducible HIF-1alpha and constitutively-expressed HIF-1beta. During hypoxic conditions, HIF-1alpha heterodimerizes with HIF-1beta and translocates to the nucleus where the HIF-1 complex binds to the hypoxia-response element (HRE) and activates expression of target genes implicated in cell growth and survival. HIF-1alpha protein expression is elevated in many solid tumors, including those of the cervix and brain, where cells that are the greatest distance from blood vessels, and therefore the most hypoxic, express the highest levels of HIF-1alpha. Therapeutic blockade of the HIF-1 signaling pathway in cancer cells therefore provides an attractive strategy for development of anticancer drugs. To identify small molecule inhibitors of the HIF-1 pathway, we have developed a cell-based reporter gene assay and screened a large compound library by using a quantitative high-throughput screening (qHTS) approach.
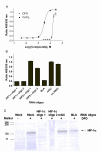
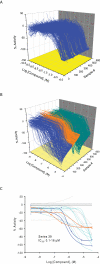
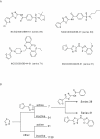
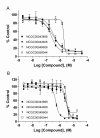
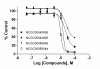
Results: The assay is based upon a beta-lactamase reporter under the control of a HRE. We have screened approximate 73,000 compounds by qHTS, with each compound tested over a range of seven to fifteen concentrations. After qHTS we have rapidly identified three novel structural series of HIF-1 pathway Inhibitors. Selected compounds in these series were also confirmed as inhibitors in a HRE beta-lactamase reporter gene assay induced by low oxygen and in a VEGF secretion assay. Three of the four selected compounds tested showed significant inhibition of hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha accumulation by western blot analysis.
Conclusion: The use of beta-lactamase reporter gene assays, in combination with qHTS, enabled the rapid identification and prioritization of inhibitors specific to the hypoxia induced signaling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of chemical compounds that induce HIF-1alpha activity.Toxicol Sci. 2009 Nov;112(1):153-63. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp123. Epub 2009 Jun 5. Toxicol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19502547 Free PMC article.
-
Using β-Lactamase and NanoLuc Luciferase Reporter Gene Assays to Identify Inhibitors of the HIF-1 Signaling Pathway.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1473:23-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6346-1_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27518620 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel small molecule inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 that differentially block hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induction in response to hypoxic stress and growth factors.Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 1;65(11):4918-28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4453. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15930314
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): a potential target for intervention in ocular neovascular diseases.Curr Drug Targets. 2013 Jul;14(8):919-35. doi: 10.2174/13894501113149990015. Curr Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23701276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular redox status regulates hypoxia inducible factor-1 activity. Role in tumour development.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Mar;26(1):39-50. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17550131 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of approved and investigational drugs that inhibit hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 16;7(7):8172-83. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6995. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26882567 Free PMC article.
-
The future of toxicity testing: a focus on in vitro methods using a quantitative high-throughput screening platform.Drug Discov Today. 2010 Dec;15(23-24):997-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.07.007. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Drug Discov Today. 2010. PMID: 20708096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Tox21 Screening Data to Evaluate the COVID-19 Drug Candidates for Their Potential Toxic Effects and Related Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 14;13:935399. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.935399. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of quinazolin-4-ones as hypoxia-inducible factor-1α inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Sep 15;21(18):5239-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.07.043. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21831635 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 in tumor angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 4;8(40):69139-69161. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19932. eCollection 2017 Sep 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28978186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

