Does switching from oral extended-release methylphenidate to the methylphenidate transdermal system affect health-related quality-of-life and medication satisfaction for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder?
- PMID: 20003260
- PMCID: PMC2796990
- DOI: 10.1186/1753-2000-3-39
Does switching from oral extended-release methylphenidate to the methylphenidate transdermal system affect health-related quality-of-life and medication satisfaction for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder?
Abstract
Background: To evaluate health-related quality of life (HRQL) and medication satisfaction after switching from a stable dose of oral extended-release methylphenidate (ER-MPH) to methylphenidate transdermal system (MTS) via a dose-transition schedule in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
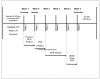
Methods: In a 4-week, multisite, open-label study, 171 children (164 in the intent-to-treat [ITT] population) aged 6-12 years diagnosed with ADHD abruptly switched from a stable dose of oral ER-MPH to MTS nominal dosages of 10, 15, 20, and 30 mg using a predefined dose-transition schedule. Subjects remained on the scheduled dose for the first week, after which the dose was then titrated to an optimal effect. The ADHD Impact Module-Children (AIM-C), a disease-specific validated HRQL survey instrument measuring child and family impact, was used to assess the impact of ADHD symptoms on the lives of children and their families at baseline and study endpoint. Satisfaction with MTS use was assessed via a Medication Satisfaction Survey (MSS) at study endpoint. Both the AIM-C and MSS were completed by a caregiver (parent/legally authorized representative). Tolerability was monitored by spontaneous adverse event (AE) reporting.
Results: AIM-C child and family HRQL mean scores were above the median possible score at baseline and were further improved at endpoint across all MTS doses. Similar improvements were noted for behavior, missed doses, worry, and economic impact AIM-C item scores. Overall, 93.8% of caregivers indicated a high level of satisfaction with their child's use of the study medication. The majority of treatment-emergent AEs (> 98%) were mild to moderate in intensity, and the most commonly reported AEs included headache, decreased appetite, insomnia, and abdominal pain. Seven subjects discontinued the study due to intolerable AEs (n = 3) and application site reactions (n = 4).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that MTS, when carefully titrated to optimal dose, may further improve child and family HRQL, as well as behavioral, medication worry, and economic impact item scores, as measured by the AIM-C in subjects switching to MTS from a stable dose of routinely prescribed oral ER-MPH after a short treatment period. Furthermore, following the abrupt conversion from oral ER-MPH to MTS, the majority of caregivers reported being highly satisfied with MTS as a treatment option for their children with ADHD.
Trial registration: NCT00151983.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transdermal therapy for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with the methylphenidate patch (MTS).CNS Drugs. 2014 Mar;28(3):217-28. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0141-y. CNS Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24532028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Switching from oral extended-release methylphenidate to the methylphenidate transdermal system: continued attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom control and tolerability after abrupt conversion.Curr Med Res Opin. 2010 Jan;26(1):129-37. doi: 10.1185/03007990903437412. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. PMID: 19916704 Free PMC article.
-
HRQL and medication satisfaction in children with ADHD treated with the methylphenidate transdermal system.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Dec;25(12):3001-10. doi: 10.1185/03007990903388797. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19849639 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term tolerability of the methylphenidate transdermal system in pediatric attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a multicenter, prospective, 12-month, open-label, uncontrolled, phase III extension of four clinical trials.Clin Ther. 2009 Aug;31(8):1844-55. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.08.002. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19808143 Clinical Trial.
-
Methylphenidate transdermal system: In attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children.Drugs. 2006;66(8):1117-26. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200666080-00007. Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16789796 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-acting methylphenidate formulations in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review of head-to-head studies.BMC Psychiatry. 2013 Sep 27;13:237. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-237. BMC Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24074240 Free PMC article.
-
An observational study of once-daily modified-release methylphenidate in ADHD: the effect of previous treatment on ADHD symptoms, other externalising symptoms and quality-of-life outcomes.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011 Oct;20 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S277-88. doi: 10.1007/s00787-011-0205-1. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21901414 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of medications on quality of life in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review.CNS Drugs. 2010 Oct;24(10):843-66. doi: 10.2165/11537450-000000000-00000. CNS Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20839896
-
Transdermal therapy for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with the methylphenidate patch (MTS).CNS Drugs. 2014 Mar;28(3):217-28. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0141-y. CNS Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24532028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents - assessment of adverse events in non-randomised studies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 9;5(5):CD012069. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012069.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29744873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold LE. Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of ADHD. Newton, PA: Handbooks in Health Care Co; 2004.
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Clinical practice guideline: Diagnosis and evaluation of the child with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics. 2000;105:1158–1170. doi: 10.1542/peds.105.5.1158. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV, Spencer T, Wilens T, Norman D, Lapey KA, Mick E, Lehman BK, Doyle A. Patterns of psychiatric comorbidity, cognition, and psychosocial functioning in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1993;150:1792–1798. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical