Effect of quinolinic acid on human astrocytes morphology and functions: implications in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20003262
- PMCID: PMC2797503
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-6-36
Effect of quinolinic acid on human astrocytes morphology and functions: implications in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
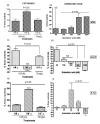
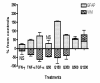
The excitotoxin quinolinic acid (QUIN) is synthesized through the kynurenine pathway (KP) by activated monocyte lineage cells. QUIN is likely to play a role in the pathogenesis of several major neuroinflammatory diseases including Alzheimer's disease (AD). The presence of reactive astrocytes, astrogliosis, increased oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines are important pathological hallmarks of AD. We assessed the stimulatory effects of QUIN at low physiological to high excitotoxic concentrations in comparison with the cytokines commonly associated with AD including IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha on primary human astrocytes. We found that QUIN induces IL-1beta expression, a key mediator in AD pathogenesis, in human astrocytes. We also explored the effect of QUIN on astrocyte morphology and functions. At low concentrations, QUIN treatment induced concomitantly a marked increase in glial fibrillary acid protein levels and reduction in vimentin levels compared to controls; features consistent with astrogliosis. At pathophysiological concentrations QUIN induced a switch between structural protein expressions in a dose dependent manner, increasing VIM and concomitantly decreasing GFAP expression. Glutamine synthetase (GS) activity was used as a functional metabolic test for astrocytes. We found a significant dose-dependent reduction in GS activity following QUIN treatment. All together, this study showed that QUIN is an important factor for astroglial activation, dysregulation and cell death with potential relevance to AD and other neuroinflammatory diseases.
Figures
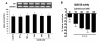
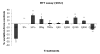
Similar articles
-
The phosphorylation status and cytoskeletal remodeling of striatal astrocytes treated with quinolinic acid.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Apr 1;322(2):313-23. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.02.024. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24583400
-
Quinolinic acid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;527:167-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0135-0_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 15206729
-
Quinolinic acid up-regulates chemokine production and chemokine receptor expression in astrocytes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;527:37-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0135-0_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 15206714
-
Implications of the kynurenine pathway and quinolinic acid in Alzheimer's disease.Redox Rep. 2002;7(4):199-206. doi: 10.1179/135100002125000550. Redox Rep. 2002. PMID: 12396664 Review.
-
Astrocytes: implications for neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011 Feb;8(1):67-80. doi: 10.2174/156720511794604543. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011. PMID: 21143158 Review.
Cited by
-
Kynurenines and Neurofilament Light Chain in Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 25;15:658202. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.658202. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34113231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Exercise Intensity on Tryptophan Metabolites in Thoroughbred Horses.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;16(1):107. doi: 10.3390/ph16010107. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678604 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Uremic Toxins on Cerebrovascular and Cognitive Disorders.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jul 22;10(7):303. doi: 10.3390/toxins10070303. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30037144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms associated with ischemic stroke severity in female mice with chronic kidney disease.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 23;9(1):6432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42933-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31015533 Free PMC article.
-
Increased 3-hydroxykynurenine serum concentrations differentiate Alzheimer's disease patients from controls.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013 Jun;263(4):345-52. doi: 10.1007/s00406-012-0384-x. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23192697
References
-
- Stone TW. Neuropharmacology of quinolinic and kynurenic acids. Pharmacol Rev. 1993;45:309–379. - PubMed
-
- Guillemin GJ, Brew BJ, Noonan CE, Knight TG, Smythe GA, Cullen KM. In: International Congress Series. Takai K, editor. Vol. 1304. 2007. Mass spectrometric detection of quinolinic acid in microdissected Alzheimer's disease plaques; pp. 404–408. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

