Insight into microRNA regulation by analyzing the characteristics of their targets in humans
- PMID: 20003303
- PMCID: PMC2799441
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-594
Insight into microRNA regulation by analyzing the characteristics of their targets in humans
Abstract
Background: microRNAs (miRNAs) are believed to regulate their targets through posttranscriptional gene regulation and have the potential to silence gene expression via multiple mechanisms. Despite previous advances on miRNA regulation of gene expression, little has been investigated from a genome scale.
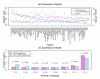
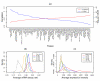
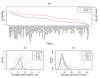
Results: To gain new insight into miRNA regulation in humans, we used large scale data and carried out a series of studies to compare various features of miRNA target genes to that of non-miRNA target genes. We observed significant differences between miRNA and non-miRNA target genes for a number of characteristics, including higher and broader mRNA expression, faster mRNA decay rate, longer protein half-life, and longer gene structures. Based on these features and by analyzing their relationships we found that miRNA target genes, other than having miRNA repression, were most likely under more complex regulation than non-miRNA target genes, which was evidenced by their higher and broader gene expression but longer gene structures. Our results of higher and broader gene expression but fast mRNA decay rates also provide evidence that miRNA dampening of the output of preexisting transcripts facilitates a more rapid and robust transition to new expression programs. This could be achieved by enhancing mRNA degradation through an additive effect from multiple miRNA targeting.
Conclusion: Genome-scale analysis on the nature of miRNA target genes has revealed a general mechanism for miRNA regulation of human gene expression. The results of this study also indicate that miRNA target genes, other than having miRNA repression, are under more complex gene regulation than non-miRNA target genes. These findings provide novel insight into miRNA regulation of human gene expression.
Figures
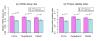
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

