Identification of known and novel pancreas genes expressed downstream of Nkx2.2 during development
- PMID: 20003319
- PMCID: PMC2799404
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-65
Identification of known and novel pancreas genes expressed downstream of Nkx2.2 during development
Abstract
Background: The homeodomain containing transcription factor Nkx2.2 is essential for the differentiation of pancreatic endocrine cells. Deletion of Nkx2.2 in mice leads to misspecification of islet cell types; insulin-expressing beta cells and glucagon-expressing alpha cells are replaced by ghrelin-expressing cells. Additional studies have suggested that Nkx2.2 functions both as a transcriptional repressor and activator to regulate islet cell formation and function. To identify genes that are potentially regulated by Nkx2.2 during the major wave of endocrine and exocrine cell differentiation, we assessed gene expression changes that occur in the absence of Nkx2.2 at the onset of the secondary transition in the developing pancreas.
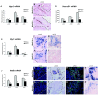
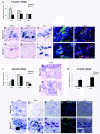
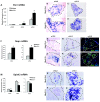
Results: Microarray analysis identified 80 genes that were differentially expressed in e12.5 and/or e13.5 Nkx2.2-/- embryos. Some of these genes encode transcription factors that have been previously identified in the pancreas, clarifying the position of Nkx2.2 within the islet transcriptional regulatory pathway. We also identified signaling factors and transmembrane proteins that function downstream of Nkx2.2, including several that have not previously been described in the pancreas. Interestingly, a number of known exocrine genes are also misexpressed in the Nkx2.2-/- pancreas.
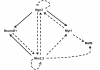
Conclusions: Expression profiling of Nkx2.2-/- mice during embryogenesis has allowed us to identify known and novel pancreatic genes that function downstream of Nkx2.2 to regulate pancreas development. Several of the newly identified signaling factors and transmembrane proteins may function to influence islet cell fate decisions. These studies have also revealed a novel function for Nkx2.2 in maintaining appropriate exocrine gene expression. Most importantly, Nkx2.2 appears to function within a complex regulatory loop with Ngn3 at a key endocrine differentiation step.
Figures

References
-
- Krapp A, Knofler M, Ledermann B, Burki K, Berney C, Zoerkler N, Hagenbuchle O, Wellauer PK. The bHLH protein PTF1-p48 is essential for the formation of the exocrine and the correct spatial organization of the endocrine pancreas. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3752–63. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.23.3752. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guz Y, Montminy MR, Stein R, Leonard J, Gamer LW, Wright CV, Teitelman G. Expression of murine STF-1, a putative insulin gene transcription factor, in beta cells of pancreas, duodenal epithelium and pancreatic exocrine and endocrine progenitors during ontogeny. Development. 1995;121:11–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

