A role of periaqueductal grey NR2B-containing NMDA receptor in mediating persistent inflammatory pain
- PMID: 20003379
- PMCID: PMC2803476
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-71
A role of periaqueductal grey NR2B-containing NMDA receptor in mediating persistent inflammatory pain
Abstract
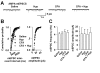
The midbrain periaqueductal grey (PAG) is a structure known for its roles in pain transmission and modulation. Noxious stimuli potentiate the glutamate synaptic transmission and enhance glutamate NMDA receptor expression in the PAG. However, little is known about roles of NMDA receptor subunits in the PAG in processing the persistent inflammatory pain. The present study was undertaken to investigate NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the PAG and their modulation to the peripheral painful inflammation. Noxious stimuli induced by hind-paw injection of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) caused up-regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the PAG, while NR2A-containing NMDA receptors were not altered. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings revealed that NMDA receptor mediated mEPSCs were increased significantly in the PAG synapse during the chronic phases of inflammatory pain in mice. PAG local infusion of Ro 25-6981, an NR2B antagonist, notably prolonged the paw withdrawal latency to thermal radian heat stimuli bilaterally in rats. Hyperoside (Hyp), one of the flavonoids compound isolated from Rhododendron ponticum L., significantly reversed up-regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the PAG and exhibited analgesic activities against persistent inflammatory stimuli in mice. Our findings provide strong evidence that up-regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the PAG involves in the modulation to the peripheral persistent inflammatory pain.
Figures



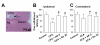

Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of NR2B receptors partially contributes to analgesic effects of Gentiopicroside in persistent inflammatory pain.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Jun;54(8):1175-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.03.007. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18410946
-
TRPV1 receptor mediates glutamatergic synaptic input to dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG) neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Jan;97(1):503-11. doi: 10.1152/jn.01023.2006. Epub 2006 Oct 25. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17065246
-
In developing hippocampal neurons, NR2B-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) can mediate signaling to neuronal survival and synaptic potentiation, as well as neuronal death.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):334-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.080. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18378405 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate-based therapeutic approaches: NR2B receptor antagonists.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;6(1):68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2005.11.001. Epub 2005 Dec 22. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16376149 Review.
-
Targeting the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B for the treatment of neuropathic pain.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Oct;6(4):693-702. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.07.008. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19789073 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of electro-acupuncture on EAAT2 and NMDAR-2B expression in goats with visceral hypersensitivity.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 2;10(23):e40700. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40700. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39717594 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced function of NR2C/2D-containing NMDA receptor in the nucleus accumbens contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain and depression in mice.Mol Pain. 2022 Jan-Dec;18:17448069211053255. doi: 10.1177/17448069211053255. Mol Pain. 2022. PMID: 35057644 Free PMC article.
-
Concentrations of oxidized linoleic acid derived lipid mediators in the amygdala and periaqueductal grey are reduced in a mouse model of chronic inflammatory pain.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018 Aug;135:128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2018.07.015. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018. PMID: 30103924 Free PMC article.
-
Hypofunction of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the periaqueductal gray contributes to nerve-injury-induced neuropathic pain.J Neurosci. 2013 May 1;33(18):7825-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5583-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23637174 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between NFκB-dependent astrocytic CXCL1 and neuron CXCR2 plays a role in descending pain facilitation.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jan 3;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1391-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30606213 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

