The role of mTOR and phospho-p70S6K in pathogenesis and progression of gastric carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study on tissue microarray
- PMID: 20003385
- PMCID: PMC2797794
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-152
The role of mTOR and phospho-p70S6K in pathogenesis and progression of gastric carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study on tissue microarray
Abstract
Background: mTOR signaling pathway and its downstream serine/threonine kinase p70S6k were frequently activated in human cancers. The dysregulation of the mTOR pathway has been found to be a contributing factor of a variety of different cancer. To investigate the role of mTOR signal pathway in the stepwise development of gastric carcinomas, we analyzed the correlations between the mTOR and P70S6K expression and clinic pathological factors and studied its prognostic role in gastric carcinomas.
Methods: mTOR and phospho-p70S6K proteins were examined by immunohistochemistry on tissue microarray containing gastric carcinomas (n = 412), adenomas (n = 47) and non-neoplastic mucosa (NNM, n = 197) with a comparison of their expression with clinicopathological parameters of carcinomas.
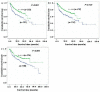
Results: There was no difference of mTOR expression between these three tissues (p > 0.05). Cytoplasmic phospho(p)-P706SK was highly expressed in adenoma, compared with ANNMs (p < 0.05), whereas its nuclear expression was lower in gastric carcinomas than gastric adenoma and ANNMs (p < 0.05). These three markers were preferably expressed in the older patients with gastric cancer and intestinal-type carcinoma (p < 0.05). mTOR expression was positively correlated with the cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of p-P70S6K(p < 0.05). Nuclear P70S6K was inversely linked to tumor size, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis and UICC staging (p < 0.05). Univariate analysis indicated that expression of mTOR and nuclear p-P70S6K was closely linked to favorable prognosis of the carcinoma patients (p < 0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that age, depth of invasion, lymphatic invasion, lymph node metastasis, Lauren's classification and mTOR expression were independent prognostic factors for overall gastric carcinomas (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Aberrant expression of p-P70S6K possibly contributes to pathogenesis, growth, invasion and metastasis of gastric carcinomas. It was considered as a promising marker to indicate the aggressive behaviors and prognosis of gastric carcinomas.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aberrant expression of cortactin and fascin are effective markers for pathogenesis, invasion, metastasis and prognosis of gastric carcinomas.Int J Oncol. 2008 Jul;33(1):69-79. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18575752
-
Downregulated parafibromin expression is a promising marker for pathogenesis, invasion, metastasis and prognosis of gastric carcinomas.Virchows Arch. 2008 Feb;452(2):147-55. doi: 10.1007/s00428-007-0551-z. Epub 2007 Dec 14. Virchows Arch. 2008. PMID: 18080135 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated Mammalian Target of Rapamycin p-mTOR Is a Favorable Prognostic Factor than mTOR in Gastric Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 22;11(12):e0168085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168085. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28005970 Free PMC article.
-
Arp2/3 overexpression contributed to pathogenesis, growth and invasion of gastric carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2008 Jul-Aug;28(4B):2225-32. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18751399
-
Paradoxical expression of maspin in gastric carcinomas: correlation with carcinogenesis and progression.Hum Pathol. 2007 Aug;38(8):1248-55. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.11.025. Epub 2007 May 8. Hum Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17490717
Cited by
-
AKT/mTOR substrate P70S6K is frequently phosphorylated in gallbladder cancer tissue and cell lines.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Oct 3;6:1373-84. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S46897. eCollection 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 24124380 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol induces cell cycle arrest by MicroRNA-21-mTOR-mediated inhibition p27 protein degradation in gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Oct 24;15:101. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0256-3. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 26500453 Free PMC article.
-
LOC285629 regulates cell proliferation and motility in colorectal cancer cells.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Jun;20(6):775-784. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1788-x. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29098557
-
Salvia plebeia R.Br. and Rosmarinic Acid Attenuate Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 18;24(3):1876. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031876. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768200 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as Regulators of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Gastric Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 27;24(7):6294. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076294. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047267 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hudes GR. mTOR as a target for therapy of renal cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2007;5:772–774. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

