Characterization of the histone H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2 isoforms in vertebrates
- PMID: 20003410
- PMCID: PMC2805615
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-86
Characterization of the histone H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2 isoforms in vertebrates
Abstract
Background: Within chromatin, the histone variant H2A.Z plays a role in many diverse nuclear processes including transcription, preventing the spread of heterochromatin and epigenetic transcriptional memory. The molecular mechanisms of how H2A.Z mediates its effects are not entirely understood. However, it is now known that H2A.Z has two protein isoforms in vertebrates, H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2, which are encoded by separate genes and differ by 3 amino acid residues.
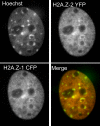
Results: We report that H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2 are expressed across a wide range of human tissues, they are both acetylated at lysine residues within the N-terminal region and they exhibit similar, but nonidentical, distributions within chromatin. Our results suggest that H2A.Z-2 preferentially associates with H3 trimethylated at lysine 4 compared to H2A.Z-1. The phylogenetic analysis of the promoter regions of H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2 indicate that they have evolved separately during vertebrate evolution.
Conclusions: Our biochemical, gene expression, and phylogenetic data suggest that the H2A.Z-1 and H2A.Z-2 variants function similarly yet they may have acquired a degree of functional independence.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of the two isoforms of the vertebrate H2A.Z histone variant.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(13):4263-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq171. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20299344 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic complementation analysis showed distinct contributions of the N-terminal tail of H2A.Z to epigenetic regulations.Genes Cells. 2016 Feb;21(2):122-35. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12327. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Genes Cells. 2016. PMID: 26833946
-
Monoubiquitylation of H2A.Z distinguishes its association with euchromatin or facultative heterochromatin.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(18):6457-68. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00241-07. Epub 2007 Jul 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17636032 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and epigenetic functions of histone variant H2A.Z.Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;87(1):19-25. doi: 10.1139/O08-117. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19234520 Review.
-
The histone variant H2A.Z in gene regulation.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019 Jun 14;12(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13072-019-0274-9. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019. PMID: 31200754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone variants and chromatin structure, update of advances.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Dec 5;21:299-311. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.12.002. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36582440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Enigma of the Histone H2A.Z-1/H2A.Z-2 Isoforms: Novel Insights and Remaining Questions.Cells. 2020 May 8;9(5):1167. doi: 10.3390/cells9051167. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32397240 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamics of Histone Modifications during Mammalian Zygotic Genome Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1459. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031459. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of histone variants in fine-tuning chromatin organization and function.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Sep;21(9):522-541. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0262-8. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32665685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMR Analyses of Acetylated H2A.Z Isoforms Identify Differential Binding Interactions with the Bromodomain of the NURF Nucleosome Remodeling Complex.Biochemistry. 2020 May 26;59(20):1871-1880. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00159. Epub 2020 May 11. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32356653 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

