Characterization of the transcripts and protein isoforms for cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein-3 (CPEB3) in the mouse retina
- PMID: 20003455
- PMCID: PMC2807433
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-109
Characterization of the transcripts and protein isoforms for cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein-3 (CPEB3) in the mouse retina
Abstract
Background: Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding proteins (CPEBs) regulate translation by binding to regulatory motifs of defined mRNA targets. This translational mechanism has been shown to play a critical role in oocyte maturation, early development, and memory formation in the hippocampus. Little is known about the presence or functions of CPEBs in the retina. The purpose of the current study is to investigate the alternative splicing isoforms of a particular CPEB, CPEB3, based on current databases, and to characterize the expression of CPEB3 in the retina.
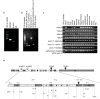
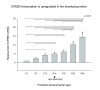
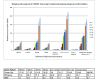
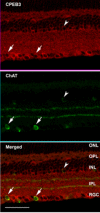
Results: In this study, we have characterized CPEB3, whose putative role is to regulate the translation of GluR2 mRNA. We identify the presence of multiple alternative splicing isoforms of CPEB3 transcripts and proteins in the current databases. We report the presence of eight alternative splicing patterns of CPEB3, including a novel one, in the mouse retina. All but one of the patterns appear to be ubiquitous in 13 types of tissue examined. The relative abundance of the patterns in the retina is demonstrated. Experimentally, we show that CPEB3 expression is increased in a time-dependent manner during the course of postnatal development, and CPEB3 is localized mostly in the inner retina, including retinal ganglion cells.
Conclusion: The level of CPEB3 was up-regulated in the retina during development. The presence of multiple CPEB3 isoforms indicates remarkable complexity in the regulation and function of CPEB3.
Figures





Similar articles
-
New Phosphospecific Antibody Reveals Isoform-Specific Phosphorylation of CPEB3 Protein.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 25;11(2):e0150000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150000. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26915047 Free PMC article.
-
The expression analysis of Sfrs10 and Celf4 during mouse retinal development.Gene Expr Patterns. 2013 Dec;13(8):425-36. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Gene Expr Patterns. 2013. PMID: 23932931 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Cpeb3 ribozyme elevates CPEB3 protein expression and polyadenylation of its target mRNAs and enhances object location memory.Elife. 2024 Feb 6;13:e90116. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90116. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38319152 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Expression of Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Proteins for the Treatment of Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2016 Nov;36(11):5673-5680. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11150. Anticancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27793888 Review.
-
Role of CPEB3 protein in learning and memory: new insights from synaptic plasticity.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jul 2;12(14):15169-15182. doi: 10.18632/aging.103404. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32619199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic Orb2A Bridges Memory Acquisition and Late Memory Consolidation in Drosophila.Cell Rep. 2015 Jun 30;11(12):1953-65. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.05.037. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26095367 Free PMC article.
-
Species-dependent splice recognition of a cryptic exon resulting from a recurrent intronic CEP290 mutation that causes congenital blindness.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 9;16(3):5285-98. doi: 10.3390/ijms16035285. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25761237 Free PMC article.
-
CPEB3 inhibits translation of mRNA targets by localizing them to P bodies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 3;116(36):18078-18087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815275116. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31416913 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative in silico analyses of cpeb1-4 with functional predictions.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2010 Aug 30;4:61-83. doi: 10.4137/bbi.s5087. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2010. PMID: 20838664 Free PMC article.
-
The ORB2 RNA-binding protein represses translation of its target transcripts during the Drosophila maternal-to-zygotic transition via its functionally conserved Zinc-binding 'ZZ' domain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 13:2025.07.10.664187. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.10.664187. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672220 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Clegg KB, Piko L. Quantitative aspects of RNA synthesis and polyadenylation in 1-cell and 2-cell mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983;74:169–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

