The hemolytic and cytolytic activities of Serratia marcescens phospholipase A (PhlA) depend on lysophospholipid production by PhlA
- PMID: 20003541
- PMCID: PMC2800117
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-261
The hemolytic and cytolytic activities of Serratia marcescens phospholipase A (PhlA) depend on lysophospholipid production by PhlA
Abstract
Background: Serratia marcescens is a gram-negative bacterium and often causes nosocomial infections. There have been few studies of the virulence factors of this bacterium. The only S. marcescens hemolytic and cytotoxic factor reported, thus far, is the hemolysin ShlA.
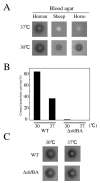
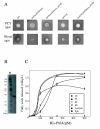
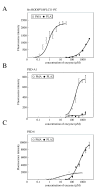
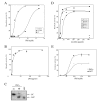
Results: An S. marcescens shlAB deletion mutant was constructed and shown to have no contact hemolytic activity. However, the deletion mutant retained hemolytic activity on human blood agar plates, indicating the presence of another S. marcescens hemolytic factor. Functional cloning of S. marcescens identified a phospholipase A (PhlA) with hemolytic activity on human blood agar plates. A phlAB deletion mutant lost hemolytic activity on human blood agar plates. Purified recombinant PhlA hydrolyzed several types of phospholipids and exhibited phospholipase A1 (PLA1), but not phospholipase A2 (PLA2), activity. The cytotoxic and hemolytic activities of PhlA both required phospholipids as substrates.
Conclusion: We have shown that the S. marcescens phlA gene produces hemolysis on human blood agar plates. PhlA induces destabilization of target cell membranes in the presence of phospholipids. Our results indicated that the lysophospholipids produced by PhlA affected cell membranes resulting in hemolysis and cell death.
Figures
References
-
- Yu VL. Serratia marcescens: historical perspective and clinical review. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1979;300:887–893. - PubMed
-
- Shinoda S, Matsuoka H, Tsuchie T, Miyoshi S, Yamamoto S, Taniguchi H, Mizuguchi Y. Purification and characterization of a lecithin-dependent haemolysin from Escherichia coli transformed by a Vibrio parahaemolyticus gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1991;137:2705–2711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

