HMGNs, DNA repair and cancer
- PMID: 20004154
- PMCID: PMC2839406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.10.007
HMGNs, DNA repair and cancer
Abstract
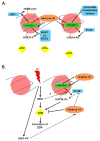
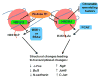
DNA lesions threaten the integrity of the genome and are a major factor in cancer formation and progression. Eukaryotic DNA is organized in nucleosome-based higher order structures, which form the chromatin fiber. In recent years, considerable knowledge has been gained on the importance of chromatin dynamics for the cellular response to DNA damage and for the ability to repair DNA lesions. High Mobility Group N1 (HMGN1) protein is an emerging factor that is important for chromatin alterations in response to DNA damage originated from both ultra violet light (UV) and ionizing irradiation (IR). HMGN1 is a member in the HMGN family of chromatin architectural proteins. HMGNs bind directly to nucleosomes and modulate the structure of the chromatin fiber in a highly dynamic manner. This review focuses mainly on the roles of HMGN1 in the cellular response pathways to different types of DNA lesions and in transcriptional regulation of cancer-related genes. In addition, emerging roles for HMGN5 in cancer progression and for HMGN2 as a potential tool in cancer therapy will be discussed.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Birger Y, Ito Y, West KL, Landsman D, Bustin M. HMGN4, a newly discovered nucleosome-binding protein encoded by an intronless gene. DNA Cell Biol. 2001;20:257–264. - PubMed
-
- Bustin M, Reeves R. High-mobility-group chromosomal proteins: architectural components that facilitate chromatin function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1996;54:35–100. - PubMed
-
- West KL, Ito Y, Birger Y, Postnikov Y, Shirakawa H, Bustin M. HMGN3a and HMGN3b, two protein isoforms with a tissue-specific expression pattern, expand the cellular repertoire of nucleosome-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:25959–25969. - PubMed
-
- Shirakawa H, Landsman D, Postnikov YV, Bustin M. NBP-45, a novel nucleosomal binding protein with a tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:6368–6374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

