Differential effects of conjugated linoleic acid isomers on the biophysical and biochemical properties of model membranes
- PMID: 20004173
- PMCID: PMC2827674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.11.020
Differential effects of conjugated linoleic acid isomers on the biophysical and biochemical properties of model membranes
Abstract
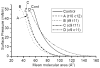
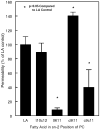
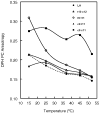
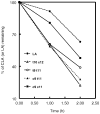
Conjugated linoleic acids (CLA) are known to exert several isomer-specific biological effects, but their mechanisms of action are unclear. In order to determine whether the physicochemical effects of CLA on membranes play a role in their isomer-specific effects, we synthesized phosphatidylcholines (PCs) with 16:0 at sn-1 position and one of four CLA isomers (trans 10 cis 12 (A), trans 9 trans 11 (B), cis 9 trans 11 (C), and cis 9 cis 11 (D)) at sn-2, and determined their biophysical properties in monolayers and bilayers. The surface areas of the PCs with the two natural CLA (A and C) were similar at all pressures, but they differed significantly in the presence of cholesterol, with PC-A condensing more than PC-C. Liposomes of PC-A similarly showed increased binding of cholesterol compared to PC-C liposomes. PC-A liposomes were less permeable to carboxyfluorescein compared to PC-C liposomes. The PC with two trans double bonds (B) showed the highest affinity to cholesterol and lowest permeability. The two natural CLA-PCs (A and C) stimulated lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activity by 2-fold, whereas the unnatural CLA-PCs (B and D) were inhibitory. These results suggest that the differences in the biophysical properties of CLA isomers A and C may partly contribute to the known differences in their biological effects.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Pariza MW. Perspective on the safety and effectiveness of conjugated linoleic acid. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:1132S–1136S. - PubMed
-
- Wahle KWJ, Heys SD, Rotondo D. Conjugated linoleic acids: are they beneficial or detrimental to health? Progress in Lipid Research. 2004;43:553–587. - PubMed
-
- Belury MA. Dietary conjugated linoleic acid in health: Physiological Effects and Mechanisms of Action. Annual Review of Nutrition. 2002;22:505–531. - PubMed
-
- House RL, Cassady JP, Eisen EJ, McIntosh MK, Odle J. Conjugated linoleic acid evokes de-lipidation through the regulation of genes controlling lipid metabolism in adipose and liver tissue. Obesity Reviews. 2005;6:247–258. - PubMed
-
- Peters JM, Park Y, Gonzalez FJ, Pariza MW. Influence of conjugated linoleic acid on body composition and target gene expression in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor [alpha]-null mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1533:233–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

