Increased intake of ethanol and dietary fat in galanin overexpressing mice
- PMID: 20004335
- PMCID: PMC2796601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.09.025
Increased intake of ethanol and dietary fat in galanin overexpressing mice
Abstract
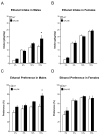
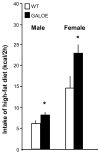
Evidence suggests that the orexigenic peptide, galanin (GAL), in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) has a role in stimulating the consumption of ethanol, in addition to a high-fat diet. This possibility was further examined in mutant mice that overexpress the GAL gene. Two sets of GAL-overexpressors (GALOE) compared with wild-type (WT) controls, maintained on laboratory chow and water, were trained to voluntarily drink increasing concentrations of ethanol, from 3 to 15%. In the GALOE versus WT mice, the results revealed the following: (1) a 35-40% increase in ethanol intake and ethanol preference, which was evident only at the highest (15%) ethanol concentration, in male but not female mice, and was seen with comparisons to littermate and nonlittermate WT controls, (2) a significantly larger, 60-75% increase in ethanol intake and ethanol preference after a day of food deprivation, again only in male GALOE mice, (3) no change in consumption of sucrose or quinine solutions in preference tests, and (4) a 55% increase in consumption of a fat-rich diet during a 2-h test period, in both male and female GALOE mice. These results obtained with overexpression of the GAL gene provide strong support for a physiological role of this peptide in stimulating the consumption of ethanol and a fat-rich diet. They reveal gender differences in the behavioral phenotype, which may reflect GAL's functional relationship to reproductive hormones in the stimulation of consummatory behavior.
Keywords: Ethanol intake; dietary fat; galanin; paraventricular nucleus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Galanin and consummatory behavior: special relationship with dietary fat, alcohol and circulating lipids.Exp Suppl. 2010;102:87-111. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0346-0228-0_8. Exp Suppl. 2010. PMID: 21299064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galanin knockout mice show disturbances in ethanol consumption and expression of hypothalamic peptides that stimulate ethanol intake.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Jan;34(1):72-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01068.x. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 19860804 Free PMC article.
-
Gonadal steroids and hypothalamic galanin and neuropeptide Y: role in eating behavior and body weight control in female rats.Endocrinology. 1998 Apr;139(4):1771-80. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.4.5867. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9528961
-
Increased caloric intake on a fat-rich diet: role of ovarian steroids and galanin in the medial preoptic and paraventricular nuclei and anterior pituitary of female rats.J Neuroendocrinol. 2007 Oct;19(10):753-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2007.01584.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17850457
-
Regulation and effects of hypothalamic galanin: relation to dietary fat, alcohol ingestion, circulating lipids and energy homeostasis.Neuropeptides. 2005 Jun;39(3):327-32. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2004.12.022. Epub 2005 Feb 1. Neuropeptides. 2005. PMID: 15944030 Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor subtype-dependent galanin actions on gamma-aminobutyric acidergic neurotransmission and ethanol responses in the central amygdala.Addict Biol. 2012 Jul;17(4):694-705. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00360.x. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Addict Biol. 2012. PMID: 21955024 Free PMC article.
-
Central nervous system regulation of food intake and energy expenditure: role of galanin-mediated feeding behavior.Neurosci Bull. 2011 Dec;27(6):407-12. doi: 10.1007/s12264-011-1841-7. Neurosci Bull. 2011. PMID: 22108817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galanin and consummatory behavior: special relationship with dietary fat, alcohol and circulating lipids.Exp Suppl. 2010;102:87-111. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0346-0228-0_8. Exp Suppl. 2010. PMID: 21299064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Converging vulnerability factors for compulsive food and drug use.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Sep 15;196:108556. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108556. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33862029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformational signatures in β-arrestin2 reveal natural biased agonism at a G-protein-coupled receptor.Commun Biol. 2018 Sep 3;1:128. doi: 10.1038/s42003-018-0134-3. eCollection 2018. Commun Biol. 2018. PMID: 30272007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams A, Clapham J, Wynick D, Speakman J. Feeding behaviour in galanin knockout mice supports a role of galanin in fat intake and preference. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008;20:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Belfer I, Hipp H, Bollettino A, McKnight C, Evans C, Virkkunen M, Albaugh B, Max M, Goldman D, Enoch M. Alcoholism is associated with GALR3 but not two other galanin receptor genes. Genes Brain Behav. 2007;6:473–481. - PubMed
-
- Brann D, Chorich L, Mahesh V. Effect of progesterone on galanin mRNA levels in the hypothalamus and the pituitary: correlation with the gonadotropin surge. Neuroendocrinology. 1993;58:531–538. - PubMed
-
- Byatt J, Staten N, Salsgiver W, Kostelc J, Collier R. Stimulation of food intake and weight gain in mature female rats by bovine prolactin and bovine growth hormone. Am J Physiol. 1993;264:E986–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

