Reduced density of calbindin immunoreactive GABAergic neurons in the occipital cortex in major depression: relevance to neuroimaging studies
- PMID: 20004363
- PMCID: PMC2823848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.10.027
Reduced density of calbindin immunoreactive GABAergic neurons in the occipital cortex in major depression: relevance to neuroimaging studies
Abstract
Background: Several lines of evidence suggest dysfunction of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic system in major depressive disorder. Neuroimaging studies report reduced levels of GABA in the dorsolateral prefrontal and occipital cortex of depressed patients. Our previous postmortem study revealed a reduction in the density and size of calbindin-immunoreactive (CB-IR) GABAergic neurons in the prefrontal cortex in major depressive disorder. The goal of this study was to test whether the changes in CB-IR neurons can also be detected in the occipital cortex, where neuroimaging studies report a prominent GABA decrease.
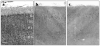
Methods: A three-dimensional cell counting probe was used to assess the cell-packing density and size of CB-IR neurons in layer II of the occipital cortex in 10 major depressive disorder subjects and 10 psychiatrically healthy control subjects.
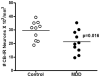
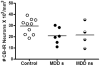
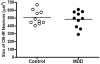
Results: The density of CB-IR neurons was significantly decreased by 28% in major depressive disorder subjects compared with the control group. The size of CB-IR neurons was unchanged in major depressive disorder subjects when compared with control subjects.
Conclusions: The reduction in the density of CB-IR GABAergic neurons in the occipital cortex in depression is similar to that observed previously in the prefrontal cortex. Deficit in cortical GABAergic interneurons may contribute to the low GABA levels detected in neuroimaging studies in major depressive disorder patients.
Copyright 2010 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sanacora G, Saricicek A. GABAergic contributions to the pathophysiology of depression and the mechanism of antidepressant action. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2007;6:127–140. - PubMed
-
- Sanacora G, Mason GF, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Hyder F, Petroff OA, et al. Reduced cortical γ-aminobutyric acid levels in depressed patients determined by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56:1043–1047. - PubMed
-
- Sanacora G, Gueorguieva R, Epperson CN, Wu YT, Appel M, Rothman DL, Krystal JH. Subtype-specific alterations of GABA and glutamate in major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:705–713. - PubMed
-
- Hasler G, van der Veen JW, Tumonis T, Meyers N, Shen J, Drevets WC. Reduced prefrontal glutamate/glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in major depression determined using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Bhagwagar Z, Wylezinska M, Jezzard P, Evans J, Ashworth F, Sule A, Matthews PM, Cowen PJ. Reduction in occipital cortex gamma-aminobutyric acid concentrations in medication-free recovered unipolar depressed and bipolar subjects. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:806–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

