A novel two-step strategy for in vitro culture of early-stage ovarian follicles in the mouse
- PMID: 20004373
- PMCID: PMC2873094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.10.027
A novel two-step strategy for in vitro culture of early-stage ovarian follicles in the mouse
Abstract
Objective: To develop an in vitro strategy to support the growth of early-stage follicles and produce mature oocytes competent for fertilization.
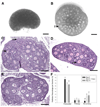
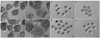
Design: Whole ovaries from 8-day-old mice were cultured for 4 days, and then secondary follicles were isolated and cultured for 12 days in a three-dimensional alginate or fibrin-alginate (FA) hydrogel matrix.
Setting: University-affiliated laboratory.
Animals: Mice.
Intervention(s): None.
Main outcome measures: Histologic evaluation of follicle development, steroid hormone production, and rates of oocyte maturation, oocyte fertilization, and embryo formation.
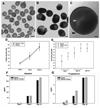
Result(s): Culture of 8-day-old mouse ovaries for 4 days resulted in transition of the follicle population from primordial and primary follicles to secondary follicles, similar to that seen in a 12-day-old ovary. Isolated secondary follicles cultured for 12 days showed larger increases in oocyte diameter and more frequent antrum formation and theca cell differentiation in the FA-hydrogel matrix compared with the alginate matrix. Steroid hormone secretion patterns were consistent with the changes in follicle morphology and cell differentiation observed in the cultured follicles. Compared with oocytes from alginate follicle cultures, a greater number of oocytes retrieved from the FA-based follicle cultures progressed to metaphase I, reached metaphase II, and could be fertilized and cleaved to two-cell embryos. The organ culture plus FA-hydrogel follicle culture strategy produced a very high rate of oocyte progression to metaphase II (88 +/- 8.7% [mean +/- SEM]) and formation of two-cell embryos (54 +/- 4%).
Conclusion(s): A strategy combining whole ovary culture of early-stage follicles and subsequent FA hydrogel in vitro follicle culture produced a high percentage of oocytes competent for fertilization; this might provide new options for fertility preservation in women and prepubertal girls facing fertility-threatening diseases or treatments.
Copyright 2010 American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Von Wolff M, Donnez J, Hovatta O, Keros V, Maltaris T, Montag M, et al. Cryopreservation and autotransplantation of human ovarian tissue prior to cytotoxic therapy--a technique in its infancy but already successful in fertility preservation. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:1547–1553. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien MJ, Pendola JK, Eppig JJ. A revised protocol for in vitro development of mouse oocytes from primordial follicles dramatically improves their developmental competence. Biol Reprod. 2003;68:1682–1686. - PubMed
-
- Wandji SA, Srsen V, Voss AK, Eppig JJ, Fortune JE. Initiation in vitro of growth of bovine primordial follicles. Biol Reprod. 1996;55:942–948. - PubMed
-
- Wandji SA, Srsen V, Nathanielsz PW, Eppig JJ, Fortune JE. Initiation of growth of baboon primordial follicles in vitro. Hum Reprod. 1997;12:1993–2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

