Adjuvant chemotherapy and timing of tamoxifen in postmenopausal patients with endocrine-responsive, node-positive breast cancer: a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 20004966
- PMCID: PMC3140679
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61523-3
Adjuvant chemotherapy and timing of tamoxifen in postmenopausal patients with endocrine-responsive, node-positive breast cancer: a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Tamoxifen is standard adjuvant treatment for postmenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer. We assessed the benefit of adding chemotherapy to adjuvant tamoxifen and whether tamoxifen should be given concurrently or after chemotherapy.
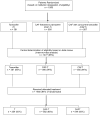
Methods: We undertook a phase 3, parallel, randomised trial (SWOG-8814, INT-0100) in postmenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, node-positive breast cancer to test two major objectives: whether the primary outcome, disease-free survival, was longer with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil (CAF) given every 4 weeks for six cycles plus 5 years of daily tamoxifen than with tamoxifen alone; and whether disease-free survival was longer with CAF followed by tamoxifen (CAF-T) than with CAF plus concurrent tamoxifen (CAFT). Overall survival and toxicity were predefined, important secondary outcomes for each objective. Patients in this open-label trial were randomly assigned by a computer algorithm in a 2:3:3 ratio (tamoxifen:CAF-T:CAFT) and analysis was by intention to treat of eligible patients. Groups were compared by stratified log-rank tests, followed by Cox regression analyses adjusted for significant prognostic factors. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00929591.
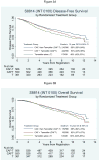
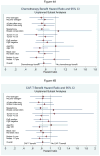
Findings: Of 1558 randomised women, 1477 (95%) were eligible for inclusion in the analysis. After a maximum of 13 years of follow-up (median 8.94 years), 637 women had a disease-free survival event (tamoxifen, 179 events in 361 patients; CAF-T, 216 events in 566 patients; CAFT, 242 events in 550 patients). For the first objective, therapy with the CAF plus tamoxifen groups combined (CAFT or CAF-T) was superior to tamoxifen alone for the primary endpoint of disease-free survival (adjusted Cox regression hazard ratio [HR] 0.76, 95% CI 0.64-0.91; p=0.002) but only marginally for the secondary endpoint of overall survival (HR 0.83, 0.68-1.01; p=0.057). For the second objective, the adjusted HRs favoured CAF-T over CAFT but did not reach significance for disease-free survival (HR 0.84, 0.70-1.01; p=0.061) or overall survival (HR 0.90, 0.73-1.10; p=0.30). Neutropenia, stomatitis, thromboembolism, congestive heart failure, and leukaemia were more frequent in the combined CAF plus tamoxifen groups than in the tamoxifen-alone group.
Interpretation: Chemotherapy with CAF plus tamoxifen given sequentially is more effective adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal patients with endocrine-responsive, node-positive breast cancer than is tamoxifen alone. However, it might be possible to identify some subgroups that do not benefit from anthracycline-based chemotherapy despite positive nodes.
Funding: National Cancer Institute (US National Institutes of Health).
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Fighting overtreatment in adjuvant breast cancer therapy.Lancet. 2009 Dec 19;374(9707):2029-2030. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62097-3. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Lancet. 2009. PMID: 20004965 No abstract available.
-
Combining and sequencing adjuvant chemotherapy and tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with node-positive breast cancer.Womens Health (Lond). 2010 May;6(3):357-60. doi: 10.2217/whe.10.22. Womens Health (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20426600 No abstract available.
-
Anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.Lancet. 2010 May 29;375(9729):1870-1; author reply 1871-2. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60867-7. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20511010 No abstract available.
-
Anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.Lancet. 2010 May 29;375(9729):1871; author reply 1871-2. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60868-9. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20511012 No abstract available.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Effects of adjuvant tamoxifen and of cytotoxic and of cytotoxic therapy on mortality in early breast cancer: an overview of 61 randomised trials among 28,896 women. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:1681–92. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 1998;351:1451–67. - PubMed
-
- National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Panel. NIH consensus development conference statement: adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, November 1–3, 2000. J National Cancer Inst. 2001;93:979–89. - PubMed
-
- Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn H-J International Consensus Panel members. Meeting Highlights: International expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer. Ann Onc. 2005;16:1569–1583. - PubMed
-
- Osborne CK. Combined chemohormonal therapy in breast cancer: a hypothesis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1981;1:121–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA022433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45466/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA28862/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA04920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46136/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA02599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35117/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12213/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA076447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35283/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077202/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35200/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA60138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52757/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35084/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52772/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76132/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA38926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77202-06/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA67663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058686/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA32734/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58686/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA052654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58723/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA03096/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

