Atypical hemispheric asymmetry in the perception of negative human vocalizations in individuals with Williams syndrome
- PMID: 20005238
- PMCID: PMC2847456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.12.002
Atypical hemispheric asymmetry in the perception of negative human vocalizations in individuals with Williams syndrome
Abstract
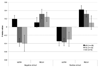
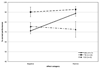
Williams syndrome is a neurological condition associated with high levels of auditory reactivity and emotional expression combined with impaired perception of prosody. Yet, little is currently known about the neural organization of affective auditory processing in individuals with this disorder. The current study examines auditory emotion processing in individuals with Williams syndrome. Hemispheric organization for positive and negative human non-linguistic sound processing was compared in participants with and without the disorder using a dichotic listening paradigm. While controls exhibited an expected right cerebral hemisphere advantage for processing negative sounds, those with Williams syndrome showed the opposite pattern. No differences between the groups emerged for the positive stimuli. The results suggest aberrant processing of negative auditory information in Williams syndrome.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adolphs R. Cognitive neuroscience of human social behavior. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2003:165–178. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Price JL, Pitkänen A, Carmichael ST. Anatomical organization of the primate amygdaloid complex. In: Aggleton JP, editor. The amygdala: Neurobiological aspects of emotion, memory and mental dysfunction. New York: Wiley; 1992. pp. 1–66.
-
- Anderson AK, Adam K, Phelps EA, Elizabeth A. Lesions of the human amygdala impair enhanced perception of emotionally salient events. Letters to Nature. 2001;41:17. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson J, Braddick O, Anker S, Curran W, Andrew R, Wattam-Bell J, Braddick F. Neurobiological models of visuospatial cognition in children with Williams syndrome: measures of dorsal-stream and frontal function. Developmental Neuropsychology. 2003;23:139–172. - PubMed
-
- Banich MT, Belger A. Interhemispheric interaction: how do the hemispheres divide and conquer a task? Cortex. 1990;26:77–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

