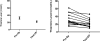Coronary artery bypass graft surgery depletes plasma thiamine levels
- PMID: 20005469
- PMCID: PMC2874825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2009.06.004
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery depletes plasma thiamine levels
Erratum in
- Nutrition. 2011 Sep;27(9):982. Salciccoli, Justin [corrected to Salciccioli, Justin]
Abstract
Objective: Thiamine is an essential component of cellular metabolism, and lack of this vitamin results in a potentially life-threatening biochemical lesion. The stress of surgery and critical disease depletes electrolytes, minerals, and essential biochemical substrates. We hypothesized that critical illness (represented by major surgery) would result in decreased thiamine levels over time.
Methods: We performed a prospective, observational study of serial thiamine levels of 15 patients who underwent non-emergent coronary artery bypass graft surgery. The primary endpoint was change in thiamine levels from before to immediately after surgery. Secondary endpoints included change in thiamine levels from presurgical to 6- and 24-h time points.
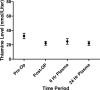
Results: Of the 15 study patients, 1 did not have a plasma thiamine measurement at time 0 because of laboratory error and could not be accounted for in paired comparisons over time. Plasma thiamine levels decreased significantly from before to after coronary artery bypass grafting (P=0.0004). In addition, there was a statistically significant decrease in thiamine levels from before surgery to 24h (P=0.003).
Conclusion: Our data suggest that major surgery (as a surrogate for the stress of critical illness) depletes thiamine levels; further study is needed to determine whether routine replacement of thiamine in the critically ill is warranted.
Figures
References
-
- Howell MD, Donnino M, Clardy P, Talmor D, Shapiro NI. Occult hypoperfusion and mortality in patients with suspected infection. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(11):1892–9. - PubMed
-
- Donnino MW, Miller J, Goyal N, Loomba M, Sankey SS, Dolcourt B, Sherwin R, Otero R, Wira C. Effective lactate clearance is associated with improved outcome in post-cardiac arrest patients. Resuscitation. 2007;75(2):229–34. - PubMed
-
- Campbell CH. Lacticacidosis and thiamine deficiency. Lancet. 1984;2(8414):1282. - PubMed
-
- Donnino M. Gastrointestinal beriberi: a previously unrecognized syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141(11):898–9. - PubMed
-
- Fried RT, Levy M, Leibowitz AB, Bronster DJ, Iberti TJ. Wernicke's encephalopathy in the intensive care patient. Crit Care Med. 1990;18(7):779–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical