Reduced IGF-1 signaling delays age-associated proteotoxicity in mice
- PMID: 20005808
- PMCID: PMC3017511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.014
Reduced IGF-1 signaling delays age-associated proteotoxicity in mice
Abstract
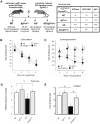
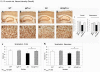
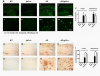
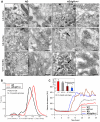
The insulin/insulin growth factor (IGF) signaling (IIS) pathway is a key regulator of aging of worms, flies, mice, and likely humans. Delayed aging by IIS reduction protects the nematode C. elegans from toxicity associated with the aggregation of the Alzheimer's disease-linked human peptide, Abeta. We reduced IGF signaling in Alzheimer's model mice and discovered that these animals are protected from Alzheimer's-like disease symptoms, including reduced behavioral impairment, neuroinflammation, and neuronal loss. This protection is correlated with the hyperaggregation of Abeta leading to tightly packed, ordered plaques, suggesting that one aspect of the protection conferred by reduced IGF signaling is the sequestration of soluble Abeta oligomers into dense aggregates of lower toxicity. These findings indicate that the IGF signaling-regulated mechanism that protects from Abeta toxicity is conserved from worms to mammals and point to the modulation of this signaling pathway as a promising strategy for the development of Alzheimer's disease therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Amaducci L, Tesco G. Aging as a major risk for degenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurol. 1994;7:283–286. - PubMed
-
- Bar-On P, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Ho G, Hashimoto M, Masliah E. Effects of the cholesterol-lowering compound methyl-beta-cyclodextrin in models of alpha-synucleinopathy. Journal of neurochemistry. 2006;98:1032–1045. - PubMed
-
- Behrends C, Langer CA, Boteva R, Bottcher UM, Stemp MJ, Schaffar G, Rao BV, Giese A, Kretzschmar H, Siegers K, et al. Chaperonin TRiC promotes the assembly of polyQ expansion proteins into nontoxic oligomers. Molecular cell. 2006;23:887–897. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard J, Martel G, Guillou JL, Nogues X, Micheau J. Impairment of spatial memory consolidation in APP(751SL) mice results in cue-guided response. Neurobiology of aging. 2008;29:1011–1021. - PubMed
-
- Bluher M, Kahn BB, Kahn CR. Extended longevity in mice lacking the insulin receptor in adipose tissue. Science. 2003;299:572–574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

