A cluster of cholinergic premotor interneurons modulates mouse locomotor activity
- PMID: 20005822
- PMCID: PMC2891428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.017
A cluster of cholinergic premotor interneurons modulates mouse locomotor activity
Abstract
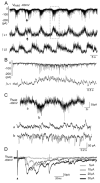
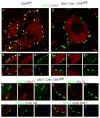
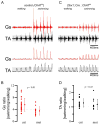
Mammalian motor programs are controlled by networks of spinal interneurons that set the rhythm and intensity of motor neuron firing. Motor neurons have long been known to receive prominent "C bouton" cholinergic inputs from spinal interneurons, but the source and function of these synaptic inputs have remained obscure. We show here that the transcription factor Pitx2 marks a small cluster of spinal cholinergic interneurons, V0(C) neurons, that represents the sole source of C bouton inputs to motor neurons. The activity of these cholinergic interneurons is tightly phase locked with motor neuron bursting during fictive locomotor activity, suggesting a role in the modulation of motor neuron firing frequency. Genetic inactivation of the output of these neurons impairs a locomotor task-dependent increase in motor neuron firing and muscle activation. Thus, V0(C) interneurons represent a defined class of spinal cholinergic interneurons with an intrinsic neuromodulatory role in the control of locomotor behavior.
Figures
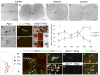

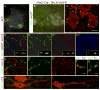
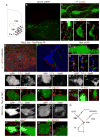

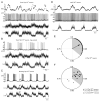


Comment in
-
A new class of spinal interneurons: the origin and function of C boutons is solved.Neuron. 2009 Dec 10;64(5):593-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.030. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 20005814
References
-
- Akay T, Acharya HJ, Fouad K, Pearson KG. Behavioral and electromyographic characterization of mice lacking EphA4 receptors. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96:642–651. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mosawie A, Wilson JM, Brownstone RM. Heterogeneity of V2-derived interneurons in the adult mouse spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;26:3003–3015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

