Hydroxyurea induces hydroxyl radical-mediated cell death in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20005847
- PMCID: PMC2821657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.024
Hydroxyurea induces hydroxyl radical-mediated cell death in Escherichia coli
Abstract
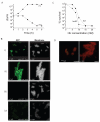
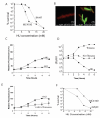
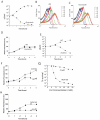
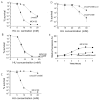
Hydroxyurea (HU) specifically inhibits class I ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), depleting dNTP pools and leading to replication fork arrest. Although HU inhibition of RNR is well recognized, the mechanism by which it leads to cell death remains unknown. To investigate the mechanism of HU-induced cell death, we used a systems-level approach to determine the genomic and physiological responses of E. coli to HU treatment. Our results suggest a model by which HU treatment rapidly induces a set of protective responses to manage genomic instability. Continued HU stress activates iron uptake and toxins MazF and RelE, whose activity causes the synthesis of incompletely translated proteins and stimulation of envelope stress responses. These effects alter the properties of one of the cell's terminal cytochrome oxidases, causing an increase in superoxide production. The increased superoxide production, together with the increased iron uptake, fuels the formation of hydroxyl radicals that contribute to HU-induced cell death.
Figures
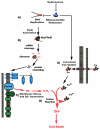
Comment in
-
Hydroxyurea triggers cellular responses that actively cause bacterial cell death.Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):728-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.027. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 20005834
References
-
- Ades SE. Regulation by destruction: design of the sigmaE envelope stress response. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008;11:535–540. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad SI, Kirk SH, Eisenstark A. Thymine metabolism and thymineless death in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1998;52:591–625. - PubMed
-
- Alba BM, Gross CA. Regulation of the Escherichia coli sigma-dependent envelope stress response. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Barbe J, Villaverde A, Guerrero R. Induction of the SOS response by hydroxyurea in Escherichia coli K12. Mutat Res. 1987;192:105–108. - PubMed
-
- Belevich I, Borisov VB, Bloch DA, Konstantinov AA, Verkhovsky MI. Cytochrome bd from Azotobacter vinelandii: evidence for high-affinity oxygen binding. Biochemistry. 2007;46:11177–11184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

