Revealing global regulatory perturbations across human cancers
- PMID: 20005852
- PMCID: PMC2900319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.016
Revealing global regulatory perturbations across human cancers
Abstract
The discovery of pathways and regulatory networks whose perturbation contributes to neoplastic transformation remains a fundamental challenge for cancer biology. We show that such pathway perturbations, and the cis-regulatory elements through which they operate, can be efficiently extracted from global gene expression profiles. Our approach utilizes information-theoretic analysis of expression levels, pathways, and genomic sequences. Analysis across a diverse set of human cancers reveals the majority of previously known cancer pathways. Through de novo motif discovery we associate these pathways with transcription-factor binding sites and miRNA targets, including those of E2F, NF-Y, p53, and let-7. Follow-up experiments confirmed that these predictions correspond to functional in vivo regulatory interactions. Strikingly, the majority of the perturbations, associated with putative cis-regulatory elements, fall outside of known cancer pathways. Our study provides a systems-level dissection of regulatory perturbations in cancer-an essential component of a rational strategy for therapeutic intervention and drug-target discovery.
Figures
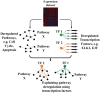
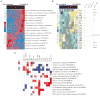
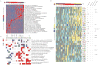

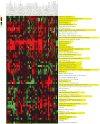

Comment in
-
A FIRE-y PAGE in the computational analysis of cancer profiles.Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):732-3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.019. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 20005836
References
-
- Adjei AA, Hidalgo M. Intracellular signal transduction pathway proteins as targets for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5386–5403. - PubMed
-
- Arora KK, Pedersen PL. Functional significance of mitochondrial bound hexokinase in tumor cell metabolism. Evidence for preferential phosphorylation of glucose by intramitochondrially generated ATP. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:17422–17428. - PubMed
-
- Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature. 2002;415:92–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

