C. elegans BED domain transcription factor BED-3 controls lineage-specific cell proliferation during organogenesis
- PMID: 20005870
- PMCID: PMC2862168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.005
C. elegans BED domain transcription factor BED-3 controls lineage-specific cell proliferation during organogenesis
Abstract
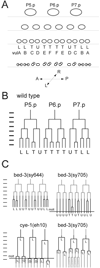
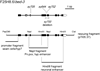
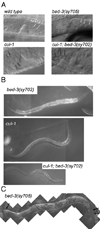
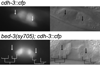
The control of cell division is critical to organogenesis, but how this control is achieved is not fully understood. We found that mutations in bed-3, encoding a BED Zn-finger domain transcription factor, confer a phenotype where a specific set of cell divisions during vulval organogenesis is lost. Unlike general cell cycle regulators in Caenorhabditis elegans, the function of bed-3 is restricted to specific lineages. Transcriptional reporters suggest that bed-3 is expressed in a limited number of cell types including vulval cells whose divisions are affected in bed-3 mutants. A bed-3 mutation also affects the expression pattern of the cdh-3 cadherin gene in the vulva. The phenotype of bed-3 mutants is similar to the phenotype caused by mutations in cog-1 (Nkx6), a component of a gene regulatory network controlling cell type specific gene expression in the vulval lineage. These results suggest that bed-3 is a key component linking the gene regulatory network controlling cell-type specification to control of cell division during vulval organogenesis.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The tailless ortholog nhr-67 regulates patterning of gene expression and morphogenesis in the C. elegans vulva.PLoS Genet. 2007 Apr 27;3(4):e69. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030069. Epub 2007 Mar 19. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17465684 Free PMC article.
-
ced-10 Rac and mig-2 function redundantly and act with unc-73 trio to control the orientation of vulval cell divisions and migrations in Caenorhabditis elegans.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 15;241(2):339-48. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0513. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784116
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans EGL-26 protein mediates vulval cell morphogenesis.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 15;241(2):247-58. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0514. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784109
-
Vulval development.WormBook. 2005 Jun 25:1-28. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.6.1. WormBook. 2005. PMID: 18050418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction during C. elegans vulval development: a NeverEnding story.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015 Jun;32:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015. PMID: 25677930 Review.
Cited by
-
A sex-specific switch in a single glial cell patterns the apical extracellular matrix.Curr Biol. 2023 Oct 9;33(19):4174-4186.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.046. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37708887 Free PMC article.
-
Morphogenesis of the caenorhabditis elegans vulva.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013 Jan-Feb;2(1):75-95. doi: 10.1002/wdev.87. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23418408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of lineage specification in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2023 Dec 6;225(4):iyad174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad174. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37847877 Free PMC article.
-
The Rice DNA-Binding Protein ZBED Controls Stress Regulators and Maintains Disease Resistance After a Mild Drought.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 18;11:1265. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01265. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33013945 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple transcription factors directly regulate Hox gene lin-39 expression in ventral hypodermal cells of the C. elegans embryo and larva, including the hypodermal fate regulators LIN-26 and ELT-6.BMC Dev Biol. 2014 May 13;14:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-14-17. BMC Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24885717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alon U. An introduction to systems biology, Design principles of biological circuits. London: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group; 2007.
-
- Aravind L. The BED finger, a novel DNA-binding domain in chromatin-boundary-element-binding proteins and transposases. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:421–423. - PubMed
-
- Chang C, Newman AP, Sternberg PW. Reciprocal EGF signaling back to the uterus from the induced C. elegans vulva coordinates morphogenesis of epithelia. Current Biology. 1999;9:237–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

