Structural basis for H3K4 trimethylation by yeast Set1/COMPASS
- PMID: 20005892
- PMCID: PMC3000633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2009.12.005
Structural basis for H3K4 trimethylation by yeast Set1/COMPASS
Abstract
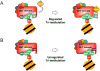
Histone methylation on lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4) is a hallmark of activity of the transcribed regions on eukaryotic chromatin. H3K4 can be mono-, di- and trimethylated by Set1/COMPASS. In this review, we will discuss recent findings regarding the role of the Y/F switch by the catalytic domain of Set1 in the regulation of H3K4 methylation by Set1/COMPASS.
Figures
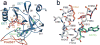
References
-
- Berger SL. Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12(2):142–8. - PubMed
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447(7143):407–12. - PubMed
-
- Dou Y, Milne TA, Ruthenburg AJ, Lee S, Lee JW, Verdine GL, Allis CD, Roeder RG. Regulation of MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferase activity by its core components. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13(8):713–9. - PubMed
-
- Dover J, Schneider J, Tawiah-Boateng MA, Wood A, Dean K, Johnston M, Shilatifard A. Methylation of histone H3 by COMPASS requires ubiquitination of histone H2B by Rad6. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(32):28368–71. - PubMed
-
- Hughes CM, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Milne TA, Copeland TD, Levine SS, Lee JC, Hayes DN, Shanmugam KS, Bhattacharjee A, Biondi CA, Kay GF, Hayward NK, Hess JL, Meyerson M. Menin associates with a trithorax family histone methyltransferase complex and with the hoxc8 locus. Mol Cell. 2004;13(4):587–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

