DNA polymerase beta-dependent long patch base excision repair in living cells
- PMID: 20006562
- PMCID: PMC2819632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.11.002
DNA polymerase beta-dependent long patch base excision repair in living cells
Abstract
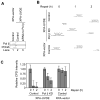
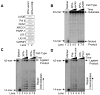
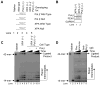
We examined a role for DNA polymerase beta (Pol beta) in mammalian long patch base excision repair (LP BER). Although a role for Pol beta is well known in single-nucleotide BER, information on this enzyme in the context of LP BER has been limited. To examine the question of Pol beta involvement in LP BER, we made use of nucleotide excision repair-deficient human XPA cells expressing UVDE (XPA-UVDE), which introduces a nick directly 5' to the cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer or 6-4 photoproduct, leaving ends with 3'-OH and 5'-phosphorylated UV lesion. We observed recruitment of GFP-fused Pol beta to focal sites of nuclear UV irradiation, consistent with a role of Pol beta in repair of UV-induced photoproducts adjacent to a strand break. This was the first evidence of Pol beta recruitment in LP BER in vivo. In cell extract, a 5'-blocked oligodeoxynucleotide substrate containing a nicked 5'-cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer was repaired by Pol beta-dependent LP BER. We also demonstrated Pol beta involvement in LP BER by making use of mouse cells that are double null for XPA and Pol beta. These results were extended by experiments with oligodeoxynucleotide substrates and purified human Pol beta.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



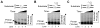


References
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. ASM Press; Washington, DC: 2006.
-
- Biade S, Sobol RW, Wilson SH, Matsumoto Y. Impairment of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent apurinic/apyrimidinic site repair on linear DNA. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1998;273:898–902. - PubMed
-
- Fortini P, Pascucci B, Parlanti E, Sobol RW, Wilson SH, Dogliotti E. Different DNA polymerases are involved in the short- and long-patch base excision repair in mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1998;37:3575–3580. - PubMed
-
- Frosina G, Fortini P, Rossi O, Carrozzino F, Raspaglio G, Cox LS, Lane DP, Abbondandolo A, Dogliotti E. Two pathways for base excision repair in mammalian cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:9573–9578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

