Chromogranin A: a new proposal for trafficking, processing and induction of granule biogenesis
- PMID: 20006653
- PMCID: PMC2825573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2009.12.007
Chromogranin A: a new proposal for trafficking, processing and induction of granule biogenesis
Abstract
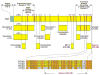
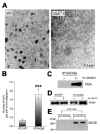
Chromogranin A (CgA), a member of the granin family serves several important cell biological roles in (neuro)endocrine cells which are summarized in this review. CgA is a "prohormone" that is synthesized at the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transported into the cisternae of this organelle via its signal peptide. It is then trafficked to the Golgi complex and then to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) where CgA aggregates at low pH in the presence of calcium. The CgA aggregates provide the physical driving force to induce budding of the TGN membrane resulting in dense core granule (DCG) formation. Within the granule, a small amount of the CgA is processed to bioactive peptides, including a predicted C-terminal peptide, serpinin. Upon stimulation, DCGs undergo exocytosis and CgA and its derived peptides are released. Serpinin, acting extracellularly is able to signal the increase in transcription of a serine protease inhibitor, protease nexin-1 (PN-1) that protects DCG proteins against degradation in the Golgi complex, which then enhances DCG biogenesis to replenish those that were released. Thus CgA and its derived peptide, serpinin, plays a significant role in granule formation and regulation of granule biogenesis, respectively, in (neuro) endocrine cells.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




Republished in
-
Reprint of: Chromogranin A: a new proposal for trafficking, processing and induction of granule biogenesis.Regul Pept. 2010 Nov 30;165(1):95-101. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.09.006. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Regul Pept. 2010. PMID: 20920534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Connor DT, Frigon RP. Chromogranin A, the major catecholamine storage vesicle soluble protein. Multiple size forms, subcellular storage, and regional distribution in chromaffin and nervous tissue elucidated by radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:3237–3247. - PubMed
-
- Zhou A, Webb G, Zhu X, Steiner DF. Proteolytic processing in the secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20745–20748. - PubMed
-
- Aardal S, Helle KB. The vasoinhibitory activity of bovine chromogranin A fragment (vasostatin) and its independence of extracellular calcium in isolated segments of human blood vessels. Regul Pept. 1992;41:9–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

