Adenovirus transport via direct interaction of cytoplasmic dynein with the viral capsid hexon subunit
- PMID: 20006841
- PMCID: PMC2810746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.11.006
Adenovirus transport via direct interaction of cytoplasmic dynein with the viral capsid hexon subunit
Abstract
Early in infection, adenovirus travels to the nucleus as a naked capsid using the microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein. How the dynein complex is recruited to viral cargo remains unclear. We find that cytoplasmic dynein and its associated proteins dynactin and NudE/NudEL, but not LIS1 or ZW10, colocalized with incoming, postendosomal adenovirus particles. However, in contrast to physiological cargos, dynein binding to adenovirus was independent of these dynein-associated proteins. Dynein itself directly interacted through its intermediate and light intermediate chains with the adenovirus capsid subunit hexon in a pH-dependent manner. Expression of hexon or injection of anti-hexon antibody inhibited virus transport but not physiological dynein function. These results identify hexon as a direct receptor for cytoplasmic dynein and demonstrate that hexon recruits dynein for transport to the nucleus by a mechanism distinct from that for physiological dynein cargo.
Figures
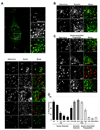

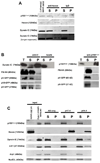

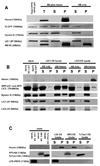
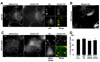
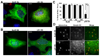
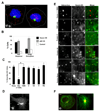
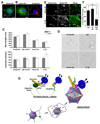
References
-
- Cotten M, Weber JM. The adenovirus protease is required for virus entry into host cells. Virology. 1995;213:494–502. - PubMed
-
- Dignam JD, Martin PL, Shastry BS, Roeder RG. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. - PubMed
-
- Dohner K, Nagel CH, Sodeik B. Viral stop-and-go along microtubules: taking a ride with dynein and kinesins. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13:320–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

