Regulation of KSHV lytic switch protein expression by a virus-encoded microRNA: an evolutionary adaptation that fine-tunes lytic reactivation
- PMID: 20006845
- PMCID: PMC2822622
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.11.008
Regulation of KSHV lytic switch protein expression by a virus-encoded microRNA: an evolutionary adaptation that fine-tunes lytic reactivation
Abstract
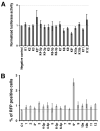
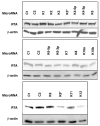
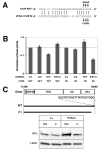
Herpesviruses encode numerous microRNAs (miRNAs), most of whose functions are unknown. The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) encodes 17 known miRNAs as part of its latency program, suggesting that these RNAs might function to regulate the latent state. Here we show that one of these KSHV miRNAs, miRK9( *), targets a sequence in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of the mRNA encoding the major lytic switch protein (RTA), which controls viral reactivation from latency. Ectopic expression of miRK9( *) impairs RTA synthesis, while its specific antagonism in latently infected cells enhances spontaneous lytic reactivation frequency by 2- to 3-fold. Mutation of the recognition sequence in the RTA 3'UTR abolishes RTA downregulation by miRK9( *). We propose that miRNA targeting of RTA, while not the primary regulator of the lytic switch, functions like a safety mechanism on the trigger of lytic reactivation, preventing stochastic variations in basal RTA transcription from activating inappropriate entry into the lytic cycle.
Figures

References
-
- Blake WJ, Balazsi G, Kohanski MA, Isaacs FJ, Murphy KF, Kuang Y, Cantor CR, Walt DR, Collins JJ. Phenotypic consequences of promoter-mediated transcriptional noise. Molecular cell. 2006;24:853–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

