Nucleosome assembly depends on the torsion in the DNA molecule: a magnetic tweezers study
- PMID: 20006952
- PMCID: PMC2793352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.09.032
Nucleosome assembly depends on the torsion in the DNA molecule: a magnetic tweezers study
Abstract
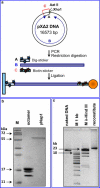
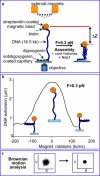
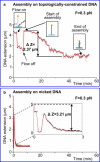
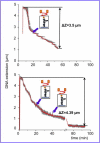
We have used magnetic tweezers to study nucleosome assembly on topologically constrained DNA molecules. Assembly was achieved using chicken erythrocyte core histones and histone chaperone protein Nap1 under constant low force. We have observed only partial assembly when the DNA was topologically constrained and much more complete assembly on unconstrained (nicked) DNA tethers. To verify our hypothesis that the lack of full nucleosome assembly on topologically constrained tethers was due to compensatory accumulation of positive supercoiling in the rest of the template, we carried out experiments in which we mechanically relieved the positive supercoiling by rotating the external magnetic field at certain time points of the assembly process. Indeed, such rotation did lead to the same nucleosome saturation level as in the case of nicked tethers. We conclude that levels of positive supercoiling in the range of 0.025-0.051 (most probably in the form of twist) stall the nucleosome assembly process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NAP1-assisted nucleosome assembly on DNA measured in real time by single-molecule magnetic tweezers.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046306. Epub 2012 Sep 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23050009 Free PMC article.
-
The supercoiling state of DNA determines the handedness of both H3 and CENP-A nucleosomes.Nanoscale. 2017 Feb 2;9(5):1862-1870. doi: 10.1039/c6nr06245h. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 28094382 Free PMC article.
-
DNA spontaneously wrapping around a histone core prefers negative supercoiling: A Brownian dynamics study.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Jan 28;21(1):e1012362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012362. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 39874389 Free PMC article.
-
The histone chaperoning pathway: from ribosome to nucleosome.Essays Biochem. 2019 Apr 23;63(1):29-43. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180055. Print 2019 Apr 23. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31015382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA mechanics and its biological impact.J Mol Biol. 2021 Mar 19;433(6):166861. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166861. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539885 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA torsion as a feedback mediator of transcription and chromatin dynamics.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):211-8. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29086. Epub 2014 May 12. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24819949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9: a single-molecule perspective.Biophys Rep. 2021 Dec 31;7(6):475-489. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2021.210021. Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 37288365 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosomes play a dual role in regulating transcription dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 9;121(28):e2319772121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2319772121. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38968124 Free PMC article.
-
NAP1-assisted nucleosome assembly on DNA measured in real time by single-molecule magnetic tweezers.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046306. Epub 2012 Sep 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23050009 Free PMC article.
-
Histone chaperone-mediated nucleosome assembly process.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 22;10(1):e0115007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115007. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25611318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Holde K.E. Springer-Verlag; New York: 1989. Chromatin.
-
- Widom J. Structure, dynamics, and function of chromatin in vitro. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1998;27:285–327. - PubMed
-
- Zlatanova J., Leuba S.H. Elsevier; Amsterdam, New York: 2004. Chromatin Structure and Dynamics: State-of-the-Art.
-
- Luger K., Mader A.W., Richmond R.K., Sargent D.F., Richmond T.J. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

