Improved viability of populations with diverse life-history portfolios
- PMID: 20007162
- PMCID: PMC2880035
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2009.0780
Improved viability of populations with diverse life-history portfolios
Abstract
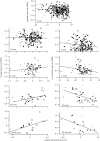
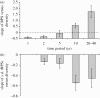
A principle shared by both economists and ecologists is that a diversified portfolio spreads risk, but this idea has little empirical support in the field of population biology. We found that population growth rates (recruits per spawner) and life-history diversity as measured by variation in freshwater and ocean residency were negatively correlated across short time periods (one to two generations), but positively correlated at longer time periods, in nine Bristol Bay sockeye salmon populations. Further, the relationship between variation in growth rate and life-history diversity was consistently negative. These findings strongly suggest that life-history diversity can both increase production and buffer population fluctuations, particularly over long time periods. Our findings provide new insights into the importance of biocomplexity beyond spatio-temporal aspects of populations, and suggest that maintaining diverse life-history portfolios of populations may be crucial for their resilience to unfavourable conditions like habitat loss and climate change.
Figures
References
-
- Araki H., Cooper B., Blouin M. S.2007Genetic effects of captive breeding cause a rapid, cumulative fitness decline in the wild. Science 318, 100–103 (doi:10.1126/science.1145621) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Battin J., Ruckelshaus M. H., Palmer R. N., Korb E., Bartz K. K., Imaki H.2007Projected impacts of climate change on salmon habitat restoration. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 6720–6725 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0701685104) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berkeley S. A., Hixon M. A., Larson R. J., Love M. S.2004Fisheries sustainability via protection of age structure and spatial distribution of fish populations. Fisheries 29, 23–32 (doi:10.1577/1548-8446(2004)29[23:FSVPOA]2.0.CO;2) - DOI
-
- Burnham K. P., Anderson D. R.2002Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach New York, NY: Springer
-
- Den Boer P.1968Spreading of risk and stabilization of animal numbers. Acta Biotheor. 18, 165–194 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
