Age-related T-cell cytokine profile parallels corneal disease severity in Sjogren's syndrome-like keratoconjunctivitis sicca in CD25KO mice
- PMID: 20007286
- PMCID: PMC2909796
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep357
Age-related T-cell cytokine profile parallels corneal disease severity in Sjogren's syndrome-like keratoconjunctivitis sicca in CD25KO mice
Abstract
Objectives: IL-2ralpha (CD25)(-/-) mice develop autoimmunity and lymphoproliferative disorders, including SS-like disease. The objective of this study was to evaluate the severity of corneal epithelial disease and T-cell cytokine profile in the ocular surface tissues of CD25KO mice.
Methods: CD25KO mice were evaluated at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age. Corneal epithelial smoothness and corneal permeability were measured. Phenotype of infiltrating lymphocytes was evaluated by immunohistochemistry. Th-1, -2 and -17 associated factors were measured by real-time PCR in cornea and conjunctiva and by Luminex immunobead assay in tears.
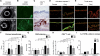
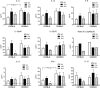
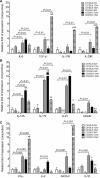
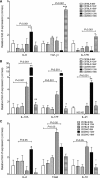
Results: Compared with 8-week-old wild-type (WT) mice, CD25KO mice of the same age had significantly greater corneal irregularity and a significant increase in the number of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells infiltrating the conjunctiva. CD25KO mice had significantly higher levels of IL-6, TGF-beta1, IL-23R, IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, CCL20, IL-10, GATA-3 and IFN-gamma mRNA transcripts in their cornea and conjunctiva than WT mice at 8 weeks. IL-17A and IL-17F mRNA transcripts peaked at 12 weeks, whereas IFN-gamma spiked at 16 weeks in CD25KO mice. Increased expression of IL-17A and IL-17F at 12 weeks in CD25KO mice was accompanied by a worsening of corneal surface parameters and an increase of CD4(+) T cell infiltrating the cornea.
Conclusions: Disruption of IL-2 signalling in CD25KO mice results in age-dependent SS-like autoimmune lacrimal-keratoconjunctivitis. A mix of Th-1 and Th-17 cytokines was detected. The peak severity of corneal epithelial disease corresponded to the peak of IL-17 expression.
Figures

References
-
- Andrianakos A, Trontzas P, Christoyannis F, et al. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in Greece: a cross-sectional population based epidemiological study. The ESORDIG Study. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:1589–601. - PubMed
-
- Zhang NZ, Shi CS, Yao QP, et al. Prevalence of primary Sjogren’s syndrome in China. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:659–61. - PubMed
-
- Thomas E, Hay EM, Hajeer A, Silman AJ. Sjogren’s syndrome: a community-based study of prevalence and impact. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37:1069–76. - PubMed
-
- Pflugfelder SC, Whitcher J, Daniels T. Sjögren’s syndrome. In: Pepose JS, Holland GN, Wilhelmus KR, editors. Ocular infection and immunity. St Louis: Mosby; 1996. pp. 1043–7.
-
- Fujita M, Igarashi T, Kurai T, Sakane M, Yoshino S, Takahashi H. Correlation between dry eye and rheumatoid arthritis activity. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;140:808–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

