Bayesian network analysis of targeting interactions in chromatin
- PMID: 20007327
- PMCID: PMC2813475
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.098822.109
Bayesian network analysis of targeting interactions in chromatin
Abstract
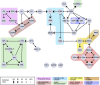
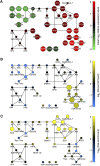
In eukaryotes, many chromatin proteins together regulate gene expression. Chromatin proteins often direct the genomic binding pattern of other chromatin proteins, for example, by recruitment or competition mechanisms. The network of such targeting interactions in chromatin is complex and still poorly understood. Based on genome-wide binding maps, we constructed a Bayesian network model of the targeting interactions among a broad set of 43 chromatin components in Drosophila cells. This model predicts many novel functional relationships. For example, we found that the homologous proteins HP1 and HP1C each target the heterochromatin protein HP3 to distinct sets of genes in a competitive manner. We also discovered a central role for the remodeling factor Brahma in the targeting of several DNA-binding factors, including GAGA factor, JRA, and SU(VAR)3-7. Our network model provides a global view of the targeting interplay among dozens of chromatin components.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A network model of the molecular organization of chromatin in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2013 Feb 21;49(4):759-71. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.040. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23438860
-
Analysis of the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) interactome in Drosophila.J Proteomics. 2014 May 6;102:137-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.03.016. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24681131
-
Distinct HP1 and Su(var)3-9 complexes bind to sets of developmentally coexpressed genes depending on chromosomal location.Genes Dev. 2003 Nov 15;17(22):2825-38. doi: 10.1101/gad.281503. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14630943 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian Su(var) genes in chromatin control.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:471-501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.042308.113225. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19575672 Review.
-
Anything else but GAGA: a nonhistone protein complex reshapes chromatin structure.Trends Genet. 2004 Jan;20(1):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2003.11.005. Trends Genet. 2004. PMID: 14698615 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of type 2 diabetes related modules and genes based on epigenetic networks.BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S5. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-S1-S5. Epub 2014 Jan 24. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 24565181 Free PMC article.
-
Global quantitative modeling of chromatin factor interactions.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Mar 27;10(3):e1003525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003525. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24675896 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors, coregulators, and epigenetic marks are linearly correlated and highly redundant.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 7;12(12):e0186324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186324. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29216191 Free PMC article.
-
A new IDH-independent hypermethylation phenotype is associated with astrocyte-like cell state in glioblastoma.Genome Biol. 2025 Jul 3;26(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13059-025-03670-y. Genome Biol. 2025. PMID: 40611337 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive models of gene regulation from high-throughput epigenomics data.Comp Funct Genomics. 2012;2012:284786. doi: 10.1155/2012/284786. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Comp Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22924024 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
