De novo expression of podocyte proteins in parietal epithelial cells during experimental glomerular disease
- PMID: 20007346
- PMCID: PMC2838596
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00428.2009
De novo expression of podocyte proteins in parietal epithelial cells during experimental glomerular disease
Abstract
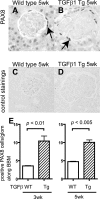
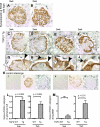
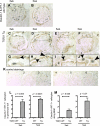
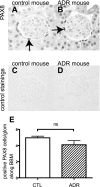
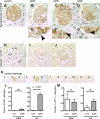
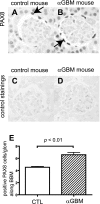
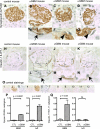
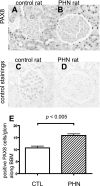
Studies have shown that certain cells of the glomerular tuft begin to express proteins considered unique to other cell types upon injury. Little is known about the response of parietal epithelial cells (PEC) to injury. To determine whether PECs change their phenotype upon injury to also express proteins traditionally considered podocyte specific, the following four models of glomerular disease were studied: the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 transgenic mouse model of global glomerulosclerosis, the adriamycin model of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), the anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) model of crescentic glomerulonephritis, and the passive Heymann nephritis model of membranous nephropathy. Double immunostaining was performed with antibodies to podocyte-specific proteins (synaptopodin and Wilms' tumor 1) and antibodies to PEC specific proteins (paired box gene 8 and claudin-1). No double staining was detected in normal mice. In contrast, the results showed a statistical increase in the number of cells attached to Bowman basement membrane that were double-positive for both podocyte/PEC proteins in TGF-beta1 transgenic, anti-GBM, and membranous animals. Double-positive cells for both podocyte and PEC proteins were also statistically increased in the glomerular tuft in TGF-beta1 transgenic, anti-GBM, and FSGS mice. These results are consistent with glomerular cells coexpressing podocyte and PEC proteins in experimental glomerular disease, but not under normal circumstances.
Figures
References
-
- Alpers CE, Hudkins KL, Gown AM, Johnson RJ. Enhanced expression of “muscle-specific” actin in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 41: 1134–1142, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Bariety J, Hill GS, Mandet C, Irinopoulou T, Jacquot C, Meyrier A, Bruneval P. Glomerular epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation in pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18: 1777–1784, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bariety J, Mandet C, Hill GS, Bruneval P. Parietal podocytes in normal human glomeruli. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 2770–2780, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Barisoni L, Kriz W, Mundel P, D'Agati V. The dysregulated podocyte phenotype: a novel concept in the pathogenesis of collapsing idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and HIV-associated nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 10: 51–61, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

