Potential involvement of P2Y2 receptor in diuresis of postobstructive uropathy in rats
- PMID: 20007349
- PMCID: PMC2838593
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00382.2009
Potential involvement of P2Y2 receptor in diuresis of postobstructive uropathy in rats
Abstract
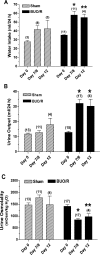
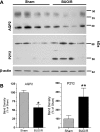
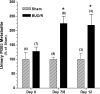
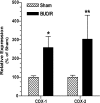
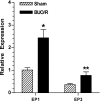
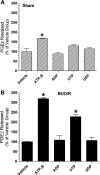
AVP resistance of the medullary collecting duct (mCD) in postobstructive uropathy (POU) has been attributed to increased production of PGE2. P2Y2 receptor activation causes production of PGE2 by the mCD. We hypothesize that increased P2Y2 receptor expression and/or activity may contribute to the diuresis of POU. Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to bilateral ureteral obstruction for 24 h followed by release (BUO/R, n = 17) or sham operation (SHM/O, n = 15) and euthanized after 1 wk or 12 days. BUO/R rats developed significant polydipsia, polyuria, urinary concentration defect, and increased urinary PGE2 and decreased aquaporin-2 protein abundance in the inner medulla compared with SHM/O rats. After BUO/R, the relative mRNA expression of P2Y2 and P2Y6 receptors was increased by 2.7- and 4.9-fold, respectively, without significant changes in mRNA expression of P2Y1 or P2Y4 receptor. This was associated with a significant 3.5-fold higher protein abundance of the P2Y2 receptor in BUO/R than SHM/O rats. When freshly isolated mCD fractions were challenged with different types of nucleotides (ATPgammaS, ADP, UTP, or UDP), BUO/R and SHM/O rats responded to only ATPgammaS and UTP and released PGE2, consistent with involvement of the P2Y2, but not P2Y6, receptor. ATPgammaS- or UTP-stimulated increases in PGE2 were much higher in BUO/R (3.20- and 2.28-fold, respectively, vs. vehicle controls) than SHM/O (1.68- and 1.30-fold, respectively, vs. vehicle controls) rats. In addition, there were significant 2.4- and 2.1-fold increases in relative mRNA expression of prostanoid EP1 and EP3 receptors, respectively, in the inner medulla of BUO/R vs. SHM/O rats. Taken together, these data suggest that increased production of PGE2 by the mCD in POU may be due to increased expression and activity of the P2Y2 receptor. Increased mRNA expression of EP1 and EP3 receptors in POU may also help accentuate PGE2-induced signaling in the mCD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential role of purinergic signaling in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 May;296(5):F1194-201. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90774.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19244398 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 receptor-mediated release of prostaglandin E2 by IMCD is altered in hydrated and dehydrated rats: relevance to AVP-independent regulation of IMCD function.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Sep;289(3):F585-92. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00050.2005. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15840771
-
Chronic dDAVP infusion in rats decreases the expression of P2Y2 receptor in inner medulla and P2Y2 receptor-mediated PGE2 release by IMCD.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Oct;289(4):F768-76. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00177.2005. Epub 2005 May 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15914777
-
P2Y2 receptor-stimulated release of prostaglandin E2 by rat inner medullary collecting duct preparations.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Oct;285(4):F711-21. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00096.2003. Epub 2003 Jun 10. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12799304
-
Interplay between renal endothelin and purinergic signaling systems.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):F666-F668. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00639.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28179257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal sodium transporter/channel expression and sodium excretion in P2Y2 receptor knockout mice fed a high-NaCl diet with/without aldosterone infusion.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):F657-68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00549.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21190950 Free PMC article.
-
A new look at electrolyte transport in the distal tubule.Annu Rev Physiol. 2012;74:325-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153225. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21888509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clopidogrel attenuates lithium-induced alterations in renal water and sodium channels/transporters in mice.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Dec;11(4):507-18. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9469-0. Epub 2015 Sep 19. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26386699 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex-1 Prevents the Downregulation of NKCC2 and ENaCα in Obstructive Kidney Disease.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 24;5:12480. doi: 10.1038/srep12480. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26207612 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y12 Receptor Localizes in the Renal Collecting Duct and Its Blockade Augments Arginine Vasopressin Action and Alleviates Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Dec;26(12):2978-87. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014010118. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25855780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoudjit L, Potapov A, Takano T. Prostaglandin E2 promotes cell survival of glomerular epithelial cells via the EP4 receptor. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290: F1534–F1542, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bao Y, Pucci ML, Chan BS, Lu R, Ito S, Schuster VL. Prostaglandin transporter PGT is expressed in cell types that synthesize and release prostanoids. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282: F1103–F1110, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsch PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol 132: 474–479, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Bomalaski JS, Clark MA. Phospholipase A2 and arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 36: 190–198, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Bonvalet JP, Pradelles P, Farman N. Segmental synthesis and actions of prostaglandins along the nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 253: F377–F387, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

