Comparative effect of direct renin inhibition and AT1R blockade on glomerular filtration barrier injury in the transgenic Ren2 rat
- PMID: 20007350
- PMCID: PMC2838585
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00373.2009
Comparative effect of direct renin inhibition and AT1R blockade on glomerular filtration barrier injury in the transgenic Ren2 rat
Abstract
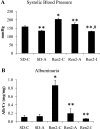
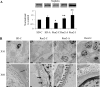
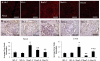
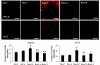
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) activation contributes to kidney injury through oxidative stress. Renin is the rate-limiting step in angiotensin (ANG II) generation. Recent work suggests renin inhibition improves proteinuria comparable to ANG type 1 receptor (AT1R) blockade (ARB). Thereby, we investigated the relative impact of treatment with a renin inhibitor vs. an ARB on renal oxidative stress and associated glomerular structural and functional changes in the transgenic Ren2 rat, which manifests hypertension, albuminuria, and increased tissue RAS activity. Young Ren2 and age-matched Sprague-Dawley (SD) controls (age 6-9 wk) were treated with a renin inhibitor (aliskiren), an ARB (irbesartan), or vehicle for 21 days. Ren2 rats exhibited increases in systolic pressure (SBP), albuminuria, and renal 3-nitrotyrosine content as well as ultrastructural podocyte foot-process effacement and diminution of the podocyte-specific protein nephrin. Structural and functional alterations were accompanied by increased renal cortical ANG II, AT1R, as well as NADPH oxidase subunit (Nox2) expression compared with SD controls. Abnormalities were attenuated to a similar extent with both aliskiren and irbesartan treatment. Despite the fact the dose of irbesartan used caused a greater reduction in SBP than aliskerin treatment (P < 0.05), the effects on proteinuria, nephrin, and oxidative stress were similar between the two treatments. Our results highlight both the importance of pressor-related reductions on podocyte integrity and albuminuria as well as RAS-mediated oxidant stress largely comparable between ARB and renin inhibition treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of renin inhibition and AT1R blockade on myocardial remodeling in the transgenic Ren2 rat.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jul;295(1):E103-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00752.2007. Epub 2008 May 6. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18460596 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of direct renin inhibition with angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade improves aldosterone but does not improve kidney injury in the transgenic Ren2 rat.Regul Pept. 2012 Jun 10;176(1-3):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Regul Pept. 2012. PMID: 22465166 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and glomerular filtration barrier injury: role of the renin-angiotensin system in the Ren2 transgenic rat.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):F1308-14. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00167.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16788142
-
Renoprotection by Direct Renin Inhibition: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 26;16(2):157-167. doi: 10.2174/1570161115666170502104809. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28464775
-
Angiotensin 2 type 1 receptor blockade different affects postishemic kidney injury in normotensive and hypertensive rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2016 Dec;72(4):813-820. doi: 10.1007/s13105-016-0514-4. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27534651 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of renin angiotensin system inhibition in kidney repair.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2010 May 4;3:7. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-3-7. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2010. PMID: 20441574 Free PMC article.
-
Decades-old renin inhibitors are still struggling to find a niche in antihypertensive therapy. A fleeting look at the old and the promising new molecules.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 May 15;28(10):115466. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115466. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32247750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restoration of the blood pressure circadian rhythm by direct renin inhibition and blockade of angiotensin II receptors in mRen2.Lewis hypertensive rats.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2012 Feb;6(1):15-29. doi: 10.1177/1753944711434039. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 22222314 Free PMC article.
-
The podocyte as a direct target for treatment of glomerular disease?Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):F46-51. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00184.2016. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27097894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin and cardiovascular disease: Worn-out path, or new direction.World J Cardiol. 2011 Mar 26;3(3):72-83. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i3.72. World J Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21499495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi S, Bigazzi R, Campese VM. Microalbuminuria in essential hypertension: significance, pathophysiology, and therapeutic implications. Am J Kidney Dis 34: 973–995, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Blundell T, Sibanda BL, Pearl L. Three-dimensional structure, specificity and catalytic mechanism of renin. Nature 304: 273–275, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Bohlender J, Menard J, Edling O, Ganten D, Luft FC. Mouse and rat plasma renin concentration and gene expression in (mRen2)27 transgenic rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 274: H1450–H1456, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Campbell DJ, Kelly DJ, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Cooper ME, Skinner SL. Increased bradykinin and “normal” angiotensin peptide levels in diabetic Sprague-Dawley and transgenic (mRen-2)27 rats. Kidney Int 56: 211–221, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Campbell DJ, Rong P, Kladis A, Rees B, Ganten D, Skinner SL. Angiotensin and bradykinin peptides in the TGR(mRen-2)27 rat. Hypertension 25: 1014–1020, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

