8-pCPT-cGMP stimulates alphabetagamma-ENaC activity in oocytes as an external ligand requiring specific nucleotide moieties
- PMID: 20007351
- PMCID: PMC2822513
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00307.2009
8-pCPT-cGMP stimulates alphabetagamma-ENaC activity in oocytes as an external ligand requiring specific nucleotide moieties
Abstract
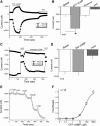
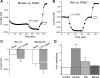
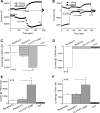
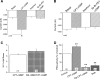
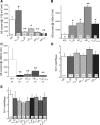
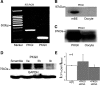
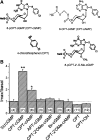
Epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) are regulated by protein kinase A, in addition to a broad spectrum of other protein kinases. It is not clear whether cGMP/PKG signaling might regulate ENaC activity. We examined the responses of alphabetagamma-ENaC channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes to 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-cGMP (8-pCPT-cGMP), a cell-permeable cGMP analog. This compound stimulated human alphabetagamma-ENaC activity in a dose-dependent fashion, but cell-impermeable cGMP had no effect. Similar stimulatory effects of cGMP were observed in oocytes expressing either mouse or rat alphabetagamma-ENaC channels. The identical ion selectivity and amiloride sensitivity of the 8-pCPT-cGMP-activated currents to those of alphabetagamma-ENaC channels suggest that the cGMP-activated currents are associated with expressed ENaC. The PKGI activator Sp isomer of beta-phenyl-1,N(2)-etheno-8-bromo-cGMP did not elicit a rise in ENaC current and that the 8-pCPT-cGMP-induced activation of ENaC channels was blocked by incubating oocytes with a PKG inhibitor, but not with other cGMP-sensitive kinase inactivators for PKA, MEK, MAP, and PKC. Surprisingly, both site-directed mutation of putative consensus PKG phosphorylation sites and truncation of entire cytosolic NH(2)- and COOH-terminal tails did not alter the response to 8-pCPT-cGMP. The ENaC activity was activated to the same extent by 8-pCPT-cGMP in cells in which PKGII expression was knocked down using small interfering RNA. Analog to 8-CPT-cAMP, 8-pCPT-cGMP was capable of activating ENaC in the identical manner in cell-free outside-out patches. We conclude that the rapid upregulation of human alphabetagamma-ENaC activity in oocytes by external 8-pCPT-cGMP and 4-chlorothiolphenol-cAMP depends on the para-chlorophenylthiol and the hydroxy groups, and 8-pCPT-cGMP may serve as a novel ENaC ligand in addition to activating PKG signal.
Figures
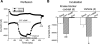
Similar articles
-
Cpt-cAMP activates human epithelial sodium channels via relieving self-inhibition.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jul;1808(7):1818-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419751 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by cGMP/PKGII.J Physiol. 2009 Jun 1;587(Pt 11):2663-76. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.170324. Epub 2009 Apr 9. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19359370 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial sodium channel enhanced osteogenesis via cGMP/PKGII/ENaC signaling in rat osteoblast.Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(4):2161-9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3065-1. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24481877
-
Stimulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by cAMP involves putative ERK phosphorylation sites in the C termini of the channel's beta- and gamma-subunit.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 14;281(15):9859-68. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512046200. Epub 2006 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16476738
-
CPT-cGMP Is A New Ligand of Epithelial Sodium Channels.Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Jan 28;12(4):359-66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.13764. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27019621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ENaC is regulated by natriuretic peptide receptor-dependent cGMP signaling.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Apr 1;304(7):F930-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00638.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23324181 Free PMC article.
-
Cpt-cAMP activates human epithelial sodium channels via relieving self-inhibition.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jul;1808(7):1818-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419751 Free PMC article.
-
Accessibility of ENaC extracellular domain central core residues.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101860. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101860. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35339489 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Na + Channels Function as Extracellular Sensors.Compr Physiol. 2024 Mar 29;14(2):1-41. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c230015. Compr Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39109974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
External Cu2+ inhibits human epithelial Na+ channels by binding at a subunit interface of extracellular domains.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 5;286(31):27436-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.232058. Epub 2011 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21659509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn YJ, Brooker DR, Kosari F, Harte BJ, Li J, Mackler SA, Kleyman TR. Cloning and functional expression of the mouse epithelial sodium channel. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 277: F121–F129, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Beckman JS, Koppenol WH. Nitric oxide, superoxide, peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 271: C1424–C1437, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Caldwell RA, Boucher RC, Stutts MJ. Neutrophil elastase activates near-silent epithelial Na+ channels and increases airway epithelial Na+ transport. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L813–L819, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

