Structural analysis of the catalytically inactive kinase domain of the human EGF receptor 3
- PMID: 20007378
- PMCID: PMC2791034
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912101106
Structural analysis of the catalytically inactive kinase domain of the human EGF receptor 3
Abstract
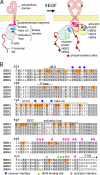
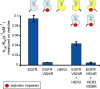
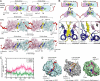
The kinase domain of human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 3/ErbB3, a member of the EGF receptor (EGFR) family, lacks several residues that are critical for catalysis. Because catalytic activity in EGFR family members is switched on by an allosteric interaction between kinase domains in an asymmetric kinase domain dimer, HER3 might be specialized to serve as an activator of other EGFR family members. We have determined the crystal structure of the HER3 kinase domain and show that it appears to be locked into an inactive conformation that resembles that of EGFR and HER4. Although the crystal structure shows that the HER3 kinase domain binds ATP, we confirm that it is catalytically inactive but can serve as an activator of the EGFR kinase domain. The HER3 kinase domain forms a dimer in the crystal, mediated by hydrophobic contacts between the N-terminal lobes of the kinase domains. This N-lobe dimer closely resembles a dimer formed by inactive HER4 kinase domains in crystal structures determined previously, and molecular dynamics simulations suggest that the HER3 and HER4 N-lobe dimers are stable. The kinase domains of HER3 and HER4 form similar chains in their respective crystal lattices, in which N-lobe dimers are linked together by reciprocal exchange of C-terminal tails. The conservation of this tiling pattern in HER3 and HER4, which is the closest evolutionary homolog of HER3, might represent a general mechanism by which this branch of the HER receptors restricts ligand-independent formation of active heterodimers with other members of the EGFR family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
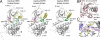

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

