Cytotoxic CD8+ T cell-neuron interactions: perforin-dependent electrical silencing precedes but is not causally linked to neuronal cell death
- PMID: 20007464
- PMCID: PMC6666122
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4339-09.2009
Cytotoxic CD8+ T cell-neuron interactions: perforin-dependent electrical silencing precedes but is not causally linked to neuronal cell death
Abstract
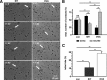
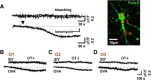
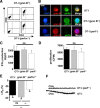
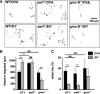
Cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells are considered important effector cells contributing to neuronal damage in inflammatory and degenerative CNS disorders. Using time-lapse video microscopy and two-photon imaging in combination with whole-cell patch-clamp recordings, we here show that major histocompatibility class I (MHC I)-restricted neuronal antigen presentation and T cell receptor specificity determine CD8(+) T-cell locomotion and neuronal damage in culture and hippocampal brain slices. Two separate functional consequences result from a direct cell-cell contact between antigen-presenting neurons and antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells. (1) An immediate impairment of electrical signaling in single neurons and neuronal networks occurs as a result of massive shunting of the membrane capacitance after insertion of channel-forming perforin (and probably activation of other transmembrane conductances), which is paralleled by an increase of intracellular Ca(2+) levels (within <10 min). (2) Antigen-dependent neuronal apoptosis may occur independently of perforin and members of the granzyme B cluster (within approximately 1 h), suggesting that extracellular effects can substitute for intracellular delivery of granzymes by perforin. Thus, electrical silencing is an immediate consequence of MHC I-restricted interaction of CD8(+) T cells with neurons. This mechanism is clearly perforin-dependent and precedes, but is not causally linked, to neuronal cell death.
Figures


References
-
- Bauer J, Bien CG, Lassmann H. Rasmussen's encephalitis: a role for autoimmune cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Curr Opin Neurol. 2002;15:197–200. - PubMed
-
- Binah O, Marom S, Rubinstein I, Robinson RB, Berke G, Hoffman BF. Immunological rejection of heart transplant: how lytic granules from cytotoxic T lymphocytes damage guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1992;420:172–179. - PubMed
-
- Brunner T, Mogil RJ, LaFace D, Yoo NJ, Mahboubi A, Echeverri F, Martin SJ, Force WR, Lynch DH, Ware CF, Green DR. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1995;373:441–444. - PubMed
-
- Choi C, Benveniste EN. Fas ligand/Fas system in the brain: regulator of immune and apoptotic responses. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004;44:65–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
