cAMP-dependent axon guidance is distinctly regulated by Epac and protein kinase A
- PMID: 20007468
- PMCID: PMC6666109
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3071-09.2009
cAMP-dependent axon guidance is distinctly regulated by Epac and protein kinase A
Abstract
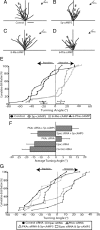
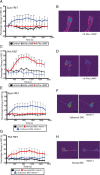
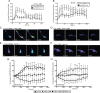
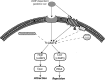
cAMP is a key mediator of a number of molecules that induce growth cone chemotaxis, including netrin-1 and myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG). Endogenous neuronal cAMP levels decline during development, and concomitantly axonal growth cones switch their response to cAMP-dependent guidance cues from attraction to repulsion. The mechanisms by which cAMP regulates these polarized growth cone responses are unknown. We report that embryonic growth cone attraction to gradients of cAMP, netrin-1, or MAG is mediated by Epac. Conversely, the repulsion conferred by MAG or netrin-1 on adult growth cones is mediated by protein kinase A (PKA). Furthermore, fluorescence resonance energy transfer reveals that netrin-1 distinctly activates Epac in embryonic growth cones but PKA in postnatal neurons. Our results suggest that cAMP mediates growth cone attraction or repulsion by distinctly activating Epac or PKA, respectively. Moreover, we propose that the developmental switch in growth cone response to gradients of cAMP-dependent guidance cues from attraction to repulsion is the result of a switch from Epac- to PKA-mediated signaling pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Bos JL. Epac: a new cAMP target and new avenues in cAMP research. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Christensen AE, Selheim F, de Rooij J, Dremier S, Schwede F, Dao KK, Martinez A, Maenhaut C, Bos JL, Genieser HG, Døskeland SO. cAMP analog mapping of Epac1 and cAMP kinase. Discriminating analogs demonstrate that Epac and cAMP kinase act synergistically to promote PC-12 cell neurite extension. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:35394–35402. - PubMed
-
- DeBellard ME, Tang S, Mukhopadhyay G, Shen YJ, Filbin MT. Myelin-associated glycoprotein inhibits axonal regeneration from a variety of neurons via interaction with sialoglycoprotein. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:89–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
