Activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta is required for hyperdopamine and D2 receptor-mediated inhibition of synaptic NMDA receptor function in the rat prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 20007479
- PMCID: PMC2832219
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3336-09.2009
Activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta is required for hyperdopamine and D2 receptor-mediated inhibition of synaptic NMDA receptor function in the rat prefrontal cortex
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 1;32(5):1914
Abstract
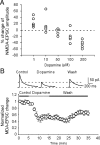
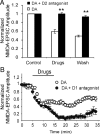
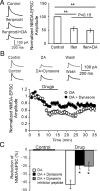
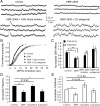
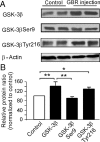
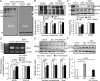
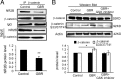
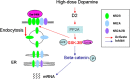
The interactions between dopamine and glutamate systems play an essential role in normal brain functions and neuropsychiatric disorders. The mechanism of NMDA receptor regulation through high concentrations of dopamine, however, remains unclear. Here, we show the signaling pathways involved in hyperdopaminergic regulation of NMDA receptor functions in the prefrontal cortex by incubating cortical slices with high concentration of dopamine or administering dopamine reuptake inhibitor 1-(2-[bis-(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl)- 4-(3-phenylpropyl)piperazine (GBR12909) in vivo. We found that, under both conditions, the synaptic NMDA receptor-mediated currents were significantly attenuated by excessive dopamine stimulation through activation of D(2) receptors. Furthermore, high dose of dopamine failed to affect NMDA receptor-mediated currents after blockade of NR2B subunits but triggered a dynamin-dependent endocytosis of NMDA receptors. The high-dose dopamine/D(2) receptor-mediated suppression of NMDA receptors was involved in the increase of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) activity, which in turn phosphorylates beta-catenin and disrupts beta-catenin-NR2B interaction, but was dependent on neither Gq11 nor PLC (phospholipase C). Moreover, the hyperdopamine induced by GBR12909 significantly decreased the expression of both surface and intracellular NR2B proteins, as well as NR2B mRNA levels, suggesting an inhibition of protein synthesis. These effects were, however, completely reversed by administration of either GSK-3beta inhibitor or D(2) receptor antagonist. These results therefore suggest that GSK-3beta is required for the hyperdopamine/D(2) receptor-mediated inhibition of NMDA receptors in the prefrontal neurons and these actions may underlie D(2) receptor-mediated psychostimulant effects and hyperdopamine-dependent behaviors in the brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dopamine D(1) receptor-mediated enhancement of NMDA receptor trafficking requires rapid PKC-dependent synaptic insertion in the prefrontal neurons.J Neurochem. 2010 Jul;114(1):62-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06720.x. Epub 2010 Mar 31. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20374423
-
Hyperdopaminergic modulation of inhibitory transmission is dependent on GSK-3β signaling-mediated trafficking of GABAA receptors.J Neurochem. 2012 Jul;122(2):308-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07790.x. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22676038 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Prenatal Poly I:C Exposure and Antipsychotics on NMDA/GABA Receptors and GSK3β-Mediated Signaling in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus of Female Rats.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;39(4):e70033. doi: 10.1111/fcp.70033. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40562368 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excitatory amino acid antagonists for acute stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;2003(3):CD001244. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001244. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 12917902 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Drugs Based on NMDAR Hypofunction Hypothesis in Schizophrenia.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 12;15:641047. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.641047. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33912003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of neuronal ion channel function by glycogen synthase kinase-3: new prospective for an old kinase.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Jul 16;5:80. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00080. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22811658 Free PMC article.
-
A role for Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3 as integrators of dopamine and serotonin neurotransmission in mental health.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012 Jan;37(1):7-16. doi: 10.1503/jpn.110011. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 21711983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LY395756, an mGluR2 agonist and mGluR3 antagonist, enhances NMDA receptor expression and function in the normal adult rat prefrontal cortex, but fails to improve working memory and reverse MK801-induced working memory impairment.Exp Neurol. 2015 Nov;273:190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.08.019. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26341392 Free PMC article.
-
GSK3β Hyperactivity during an Early Critical Period Impairs Prefrontal Synaptic Plasticity and Induces Lasting Deficits in Spine Morphology and Working Memory.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Dec;41(13):3003-3015. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.110. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27353310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen PH. The dopamine uptake inhibitor GBR 12909: selectivity and molecular mechanism of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989;166:493–504. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Marion S, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG. An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell. 2005;122:261–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
