A peripheral neuroimmune link: glutamate agonists upregulate NMDA NR1 receptor mRNA and protein, vimentin, TNF-alpha, and RANTES in cultured human synoviocytes
- PMID: 20007519
- PMCID: PMC2838657
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00452.2009
A peripheral neuroimmune link: glutamate agonists upregulate NMDA NR1 receptor mRNA and protein, vimentin, TNF-alpha, and RANTES in cultured human synoviocytes
Abstract
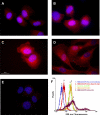
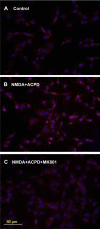
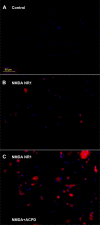
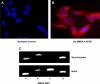
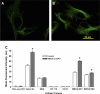
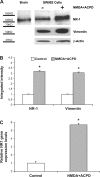
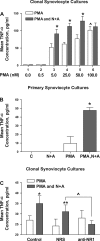
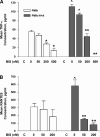
Human primary and clonal synovial cells were incubated with glutamate receptor agonists to assess their modulating influence on glutamate receptors N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) NR1 and NR2 and inflammatory cytokines to determine potential for paracrine or autocrine (neurocrine) upregulation of glutamate receptors, as has been shown for bone and chondrocytes. Clonal SW982 synoviocytes constitutively express vimentin, smooth muscle actin (SMA), and NMDA NR1 and NR2. Coincubation (6 h) with glutamate agonists NMDA (5 microM), and the NMDA NR1 glycine site activator (+/-)1-aminocyclopentane-cis-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (5 muM), significantly increases cellular mRNA and protein levels of glutamate receptors, as well as increasing vimentin, SMA, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted), assessed qualitatively and quantitatively with nucleotide amplification, image analysis of immunocytochemical staining, fluorescein-activated cell sorting, Western blotting, and immunoassays. Human primary synovial cells harvested from patients with arthritic conditions also constitutively expressed NMDA NR1 with increases after agonist treatment. Glutamate receptor agonist-induced increases were blocked by the noncompetitive glutamate antagonist MK-801 (8 microg/ml) and NR1 blocking antibody. Coincubation with glutamate agonists and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, a protein kinase C activator, significantly enhanced mean levels of TNF-alpha and RANTES in SW982 cell supernatants compared with incubation with either agent alone. Increases were diminished with protein kinase inhibitor and NR1 blocking antibody. The functional activation of glutamate receptors on human synoviocytes establishes a neurogenic cell signaling link between neurotransmitter glutamate released from nerve terminals and target cells in the joint capsule. The influence of glutamate on subsequent release of cellular proinflammatory mediators in non-neural tissue for activation of downstream immune events supports a peripheral neuroimmune link in arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental changes in glutamate receptor-activated translocation of protein kinase C in cerebellar granule neurons.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1996 Jun 14;94(1):22-30. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(96)00039-9. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8816273
-
The metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist 1S,3R-ACPD stimulates and modulates NMDA receptor mediated excitotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures.Brain Res. 2001 Apr 13;898(1):91-104. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02148-5. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11292452
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate autoreceptors respond to low and high agonist concentrations by facilitating, respectively, exocytosis and carrier-mediated release of glutamate in rat hippocampus.J Neurosci Res. 2007 Dec;85(16):3657-65. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21446. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17671992
-
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 accelerates NMDA receptor trafficking.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 15;21(16):6058-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-06058.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11487629 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the NR3A subunit on NMDA receptor functions.Prog Neurobiol. 2010 May;91(1):23-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20097255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AMPA/kainate glutamate receptor antagonists prevent posttraumatic osteoarthritis.JCI Insight. 2020 Jul 9;5(13):e134055. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.134055. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32544091 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in joint damage induced by Brucella abortus infection through production and induction of matrix metalloproteinases.Infect Immun. 2011 Sep;79(9):3619-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05408-11. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21730088 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β genes in the cochlea and inferior colliculus in salicylate-induced tinnitus.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Apr 9;8:30. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-30. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21477330 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of central and peripheral TRPV1 and ROS levels on proinflammatory mediators and nociceptive behavior.Mol Pain. 2010 Aug 6;6:46. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-46. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20691059 Free PMC article.
-
Coupled cell networks are target cells of inflammation, which can spread between different body organs and develop into systemic chronic inflammation.J Inflamm (Lond). 2015 Jul 25;12:44. doi: 10.1186/s12950-015-0091-2. eCollection 2015. J Inflamm (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26213498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Behr TM, Spes CH, Pongratz DE, Weiss M, Meiser B, Uberfuhr P, Theisen K, Angermann CE. Adult human cardiomyocytes coexpress vimentin and Ki67 in heart transplant rejection and in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Heart Lung Transplant 17: 795–800, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Chenu C, Serre CM, Raynal C, Burt-Pichat B, Delmas PD. Glutamate receptors are expressed by bone cells and are involved in bone resorption. Bone 22: 295–299, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Dougherty PM, Sluka KA, Sorkin LS, Westlund KN, Willis WD. Neural changes in acute arthritis in monkeys. I. Parallel enhancement of responses of spinothalamic tract neurons to mechanical stimulation and excitatory amino acids. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 17: 1–13, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Flood S, Parri R, Williams A, Duance V, Mason D. Modulation of interleukin-6 and matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes by functional ionotropic glutamate receptors. Arthritis Rheum 56: 2523–2534, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

