Inflammasome-associated nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat proteins and inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 20007570
- PMCID: PMC3666034
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902425
Inflammasome-associated nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat proteins and inflammatory diseases
Abstract
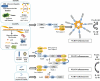
The nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat (NLR) proteins are a recently discovered family of intracellular pathogen and danger signal sensors. NLRs have emerged as important contributors to innate immunity in animals. The physiological impact of these genes is increasingly evident, underscored by the genetic association of variant family members with an array of inflammatory diseases. The association of mutations in NLR genes with autoinflammatory diseases indicates an important function of these genes in inflammation in vivo. This review summarizes the role of the inflammasome NLR proteins in innate immunity and inflammatory diseases and explores the possible utility of some of these NLRs as pharmacological targets.
Figures

References
-
- Martinon F, Mayor A, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes: guardians of the body. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009;27:229–265. - PubMed
-
- Ogura Y, Sutterwala FS, Flavell RA. The inflammasome: first line of the immune response to cell stress. Cell. 2006;126:659–662. - PubMed
-
- Ting JP, Davis BK. CATERPILLER: a novel gene family important in immunity, cell death, and diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005;23:387–414. - PubMed
-
- Ting JP, Kastner DL, Hoffman HM. CATERPILLERs, pyrin and hereditary immunological disorders. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006;6:183–195. - PubMed
-
- Amer A, Franchi L, Kanneganti TD, Body-Malapel M, Ozoren N, Brady G, Meshinchi S, Jagirdar R, Gewirtz A, Akira S, Nunez G. Regulation of Legionella phagosome maturation and infection through flagellin and host Ipaf. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:35217–35223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

