Asynchronous RAG-1 expression during B lymphopoiesis
- PMID: 20007571
- PMCID: PMC2796202
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902333
Asynchronous RAG-1 expression during B lymphopoiesis
Abstract
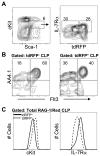
Changes in cell surface markers and patterns of gene expression are commonly used to construct sequences of events in hematopoiesis. However, the order may not be as rigid as once thought and it is unclear which changes represent the best milestones of differentiation. We developed a fate-mapping model where cells with a history of RAG-1 expression are permanently marked by red fluorescence. This approach is valuable for appreciating lymphoid-lineage relationships without need for irradiation and transplantation. Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) as well as myeloid and dendritic cell progenitors were unlabeled. Also as expected, most previously identified RAG-1(+) early lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow and all lymphoid-affiliated cells were marked. Of particular interest, there was heterogeneity among canonical common lymphoid progenitors (CLP) in bone marrow. Labeled CLP expressed slightly higher levels of IL-7Ralpha, displayed somewhat less c-Kit, and generated CD19(+) lymphocytes faster than the unlabeled CLP. Furthermore, CLP with a history of RAG-1 expression were much less likely to generate dendritic and NK cells. The RAG-1-marked CLP were lineage stable even when exposed to LPS, while unlabeled CLP were redirected to become dendritic cells in response to this TLR4 ligand. These findings indicate that essential events in B lymphopoiesis are not tightly synchronized. Some progenitors with increased probability of becoming lymphocytes express RAG-1 while still part of the lineage marker-negative Sca-1(+)c-Kit(high) (LSK) fraction. Other progenitors first activate this locus after c-Kit levels have diminished and cell surface IL-7 receptors are detectable.
Figures





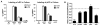

References
-
- Blijlevens NM, Donnelly JP, De Pauw BE. Prospective evaluation of gut mucosal barrier injury following various myeloablative regimens for haematopoietic stem cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005;35:707–711. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz BA, Sambandam A, Maillard I, Harman BC, Love PE, Bhandoola A. Selective thymus settling regulated by cytokine and chemokine receptors. J. Immunol. 2007;178:2008–2017. - PubMed
-
- Manz MG, Traver D, Miyamoto T, Weissman IL, Akashi K. Dendritic cell potentials of early lymphoid and myeloid progenitors. Blood. 2001;97:3333–3341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

